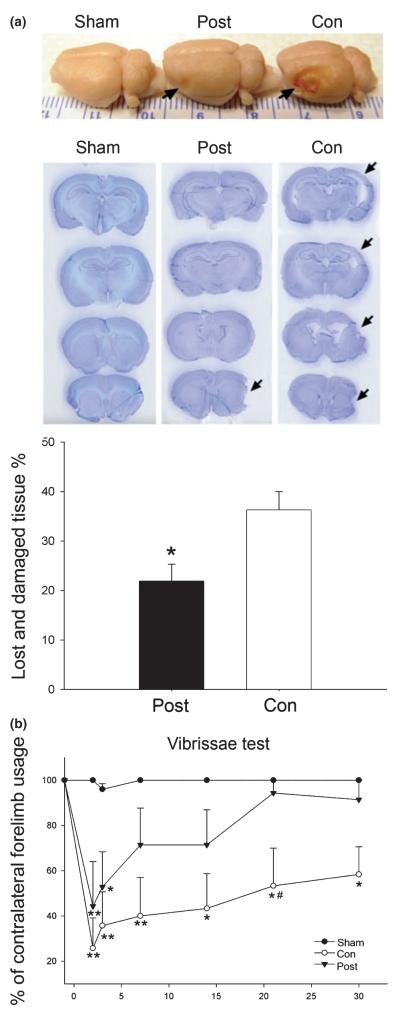
Fig. 2.
Long-term protective effect of postconditioning. (a). Post-conditioning reduced ischemic damage up to 1 month after focal ischemia. Representative whole brains (top) and the cresyl violet staining of four coronal sections (second panel) from rats that received sham surgery, postconditioning, or control ischemia are presented. Arrows indicate injury sites. A bar graph (third panel) presents average lesion sizes measured 1 month after ischemia. Postconditioning reduced infarction from 36 ± 4% (n = 6) to 22 ± 3% (n = 7) in control ischemic animals (*p = 0.006, postconditioning vs. control). Post, ischemia plus postconditioning; Con, control ischemia without postconditioning. (b). Postconditioning attenuates the asymmetrical behavioral abnormalities measured up to 1 month after stroke. In the vibrissae test, the number of contralateral forelimb placements was compared with that of the ipsilateral forelimb, n = 5–7/group. Postconditioning attenuates the overall deficit from 2 to 30 days after stroke (two-way ANOVA, p < 0.001). *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 versus sham (one-way repeated measures ANOVA); #p < 0.05 versus postconditioning at 21 days (two-way ANOVA, Student—Newman—Keuls).