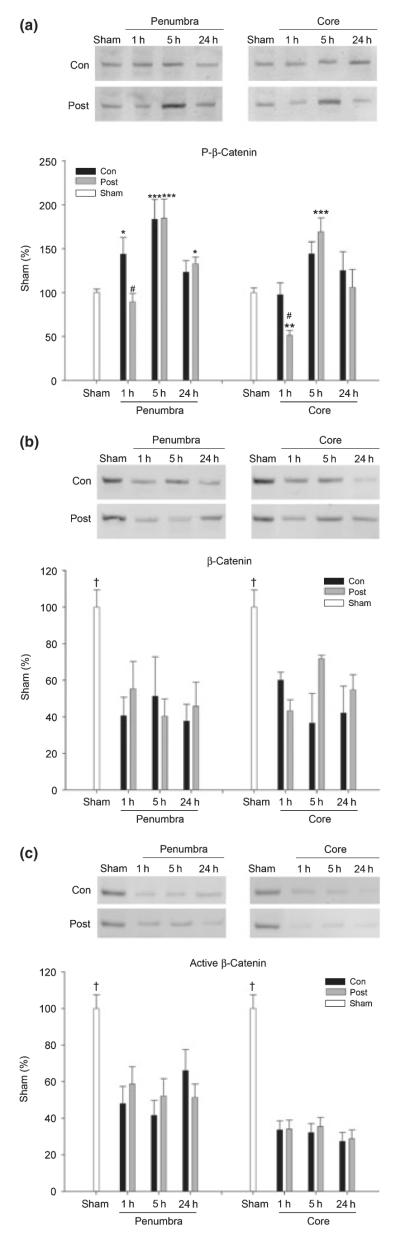
Fig. 5.
Effects of postconditioning on levels of phosphorylated, total, and active β-catenin after stroke. Western blot protein bands and corresponding mean optical densities (bar graphs) are shown. (a) Phosphorylated-β-catenin levels postischemia with and without postconditoning. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus sham; and #p < 0.05, versus 1 h/con. (b) Decreased levels of β-catenin postischemia. An antibody that recognizes total β-catenin was used for detection.†p < 0.05 versus other time points, n = 3–5/group. (c) Decreased levels of active β-catenin postischemia. An antibody recognizing the active, non-phosphorylated form of β-catenin was used for detection. †p < 0.05 versus other time points, n = 3–5/group.