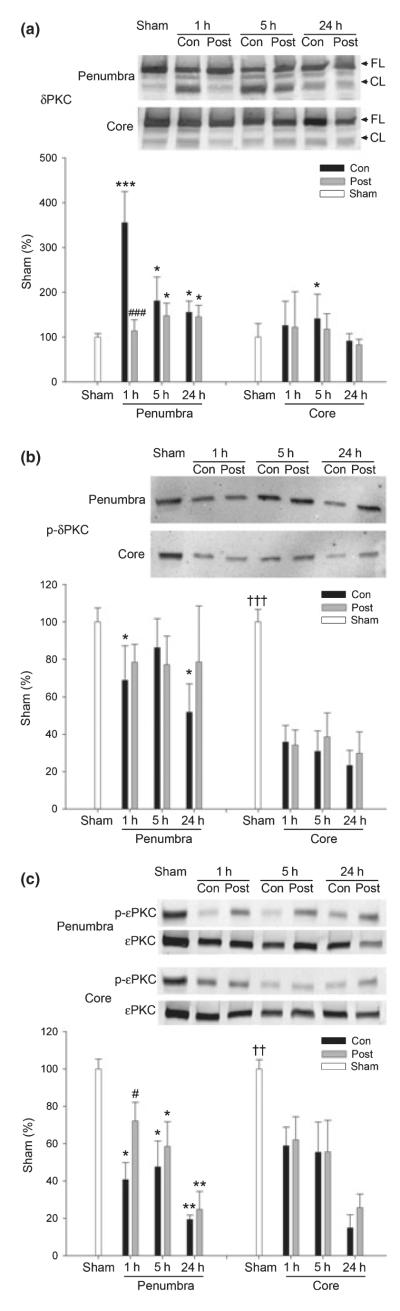
Fig. 7.
The effect of postconditioning on the protein kinase C (PKC) pathway. Representative western blot protein bands (top panels) and corresponding mean optical densities, normalized to same protein in sham rats (bar graphs) are shown. (a) Postconditioning reduced δPKC cleavage in the ischemic penumbra. The levels of cleaved δPKC were increased in the ischemic penumbra after stroke (see bar graph). The increase at 1 h was significantly inhibited by postconditioning. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 versus sham; ###p < 0.001 versus 1 h/control, n = 5–10/group. (b) Phosphorylated-δPKC level decreased postischemia. No significant difference was found between control ischemia and postconditioning. *p < 0.05 versus sham. †††p < 0.001 versus the rest of the groups in the core, n = 3–5/group. (c) Postconditioning increased P-εPKC levels at 1 h compared with control ischemia. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus sham; #p < 0.05 versus 1 h/con; ††p < 0.01 versus the rest of the groups in the core, n = 3– 10/group.