Figure 4. The Fate of N-Terminally Extended X6[QL9] and the Final QL9 Peptide Is Determined by ERAAP and the Ld MHC Molecule.
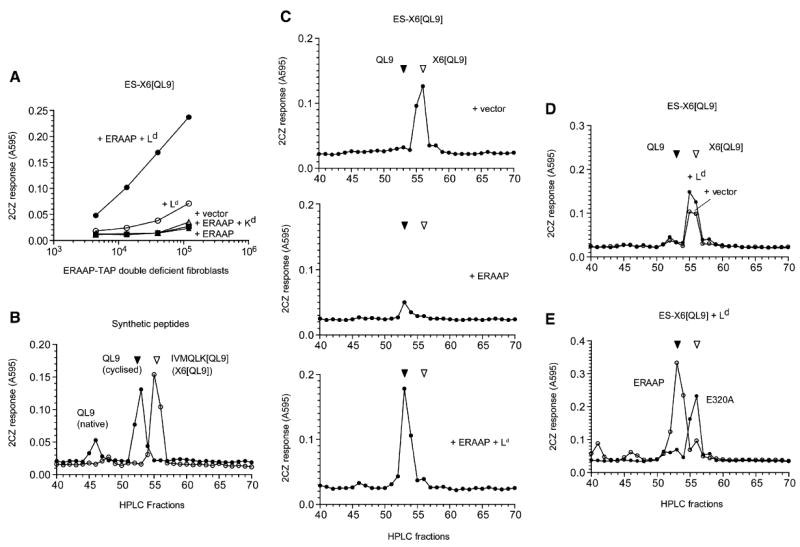
(A) Generation of the QL9-Ld complex in ERAAP-TAP double-deficient fibroblasts from the ER-targeted ES-X6[QL9] precursor requires ERAAP and the Ld MHC. The ERAAP-TAP double-deficient fibroblasts were cotransfected with the ES-X6[QL9] precursor and other cDNAs shown. Expression of the QL9-Ld complex was detected with lacZ-inducible 2CZ T cell hybridoma as in Figure 1.
(B) Synthetic IVMQLK[QL9] and the QL9 peptides can be resolved by HPLC and detected by 2CZ T cells. 10 fmoles of indicated peptides were injected into the HPLC. Each fraction was treated with trypsin and assayed with 2CZ T cells and Ld-L cells as APCs.
(C) ERAAP generates the final QL9 peptide from the X6[QL9] precursor in the presence of Ld but degrades the precursor peptide in the absence of Ld. The ERAAP-TAP double-deficient fibroblasts were cotransfected with the ES-X6[QL9] precursor construct and either vector alone, ERAAP alone, or ERAAP plus Ld. The peptides were extracted from the transfected cells and fractionated by HPLC. Each fraction was treated with trypsin and used to stimulate 2CZ T cells in the presence of Ld-L cells as APCs.
(D) The absence of ERAAP cannot be compensated by other proteases. The ERAAP-TAP double-deficient fibroblasts were transfected with the ES-X6[QL9] construct with either vector alone or Ld, and cell extracts were analyzed for 2CZ activation after HPLC fractionation and trypsin treatment of each fraction.
(E) Generation of the final QL9 peptide from its X6[QL9] precursor in the presence of Ld requires enzymatically active ERAAP. The ERAAP-TAP double-deficient fibroblasts were cotransfected with the ES-X6[QL9] precursor, Ld, and either hERAAP WT or its enzymatically inactive mutant E320A. The cell extracts were analyzed for 2CZ activation after HPLC fractionation and trypsin treatment. Data are representative of at least three (C) or two independent experiments.
