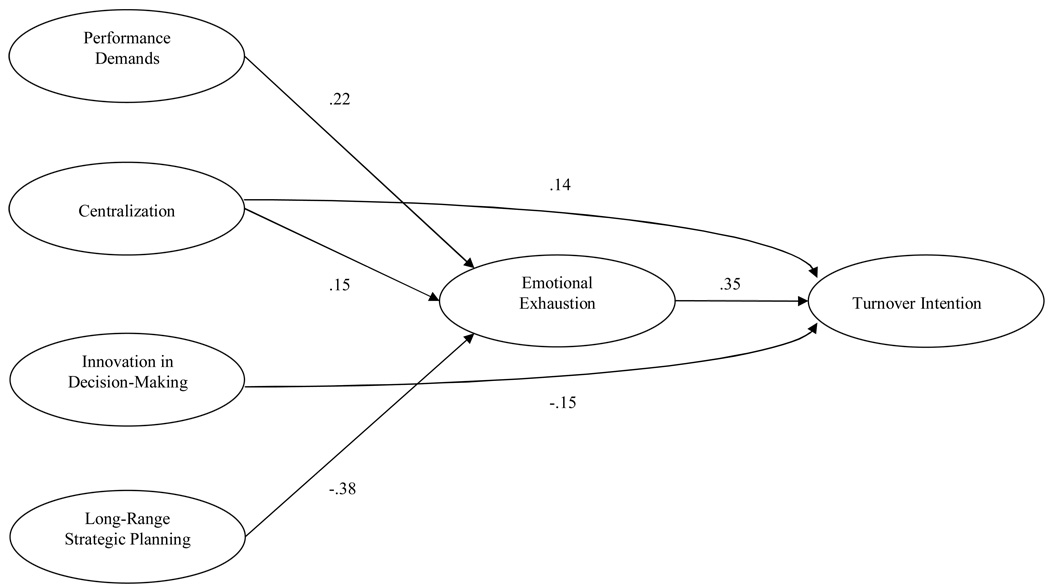
Fig. 1.
Significant paths in trimmed model of emotional exhaustion and turnover intention with maximum likelihood estimates (standardized, p < .05, two-tailed). Note. Correlations among the exogenous variables are not shown. Relationships of emotional exhaustion and turnover intention on the control variables are not shown.