Figure 1. A 3 subunit human Ska1 complex localizes to outer kinetochore and microtubules.
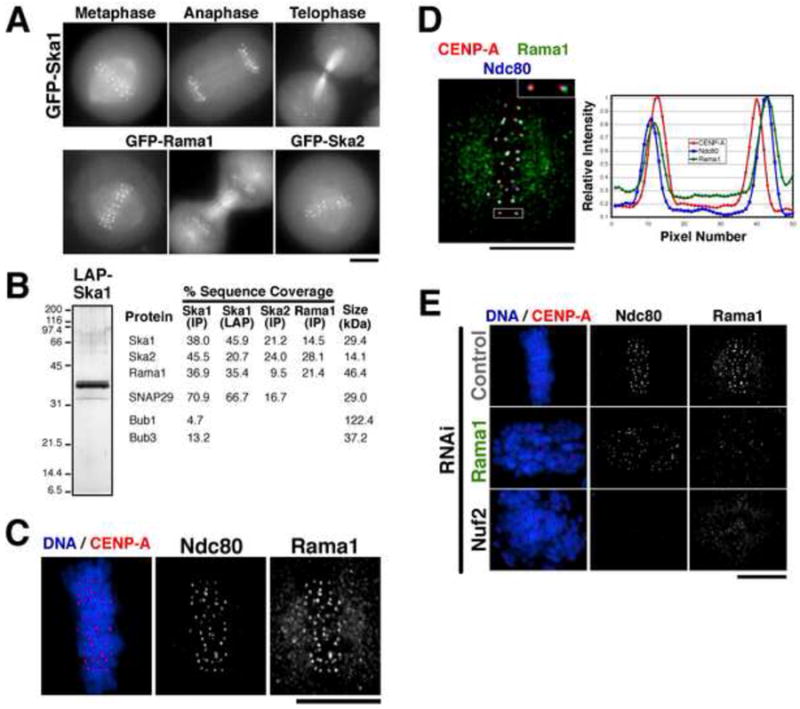
(A) Images of mitotic cells from clonal human cell lines stably expressing moderate amounts of Ska1, Ska2, and Rama1 as GFPLAP fusions. Each fusion protein localizes to kinetochores and microtubules throughout mitosis. (B) Purification of a 3-subunit Ska1 complex. GFPLAP tagged fusions were used to isolate Ska1, Ska2, or Rama1 from the stable cell lines shown in (A) using either one step IPs, or tandem affinity (LAP) purifications. Left, silver stained gel of the Ska1 LAP purification. Right, percent sequence coverage from the mass spectrometric analysis of these samples of proteins identified in the Ska1 complex purifications, but not unrelated controls. (C) Localization of endogenous Rama1. Immunofluorescence using anti-Rama1, anti-HEC1, and anti-GFP (against GFP-CENP-A) antibodies. Rama1 shows a punctuate cellular background staining throughout the cell cycle, but shows pronounced mitotic localization to kinetochores following after nuclear envelope breakdown. (D) Left, merged image showing co-localization of GFP-CENP-A, Rama1, and HEC1. Right, graph showing a linescan of the fluorescent intensity of the highlighted kinetochore. Rama1 co-localizes with Hec1 at the outer kinetochore, and localizes peripherally to CENP-A. (E) Rama1 kinetochore localization depends on the Ndc80 complex, but the Ndc80 complex localizes to kinetochores independently of Rama1. Immunofluorescence of control cells, Rama1 depleted cells, and Nuf2 depleted cells showing localization of GFP-CENP-A, Ndc80/HEC1, and Rama1. Scale bars, 10 μm.
