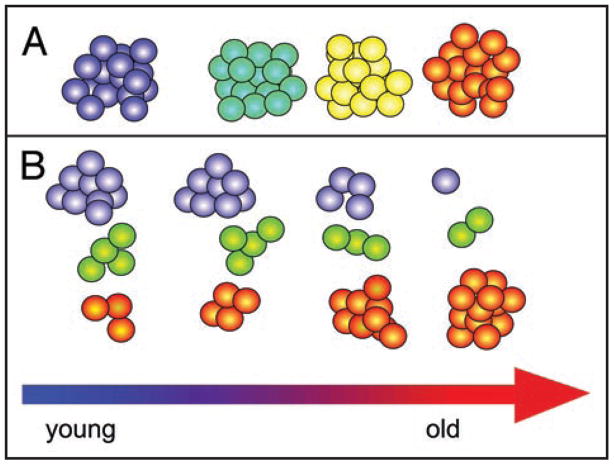
Figure 1.
Models of HSC aging. (A) The classical model assumes a homogenous population of HSC. All of these HSC progressively change their behavior as a result of aging (blue corresponds to young; orange to old). (B) The new model of HSC aging builds on the insight that HSC are heterogeneous and that the representation of the different classes of HSC shifts during aging.24 The young HSC compartment is dominated by Ly-bi HSC (Blue), while the aged HSC accumulates My-bi HSC (orange). Bala HSC (green) have an intermediate lifespan.25 The changing combination of the different types of HSC (B) generates the averaged behavior of the HSC compartment (A) during the life of the organism.