Fig. 3.
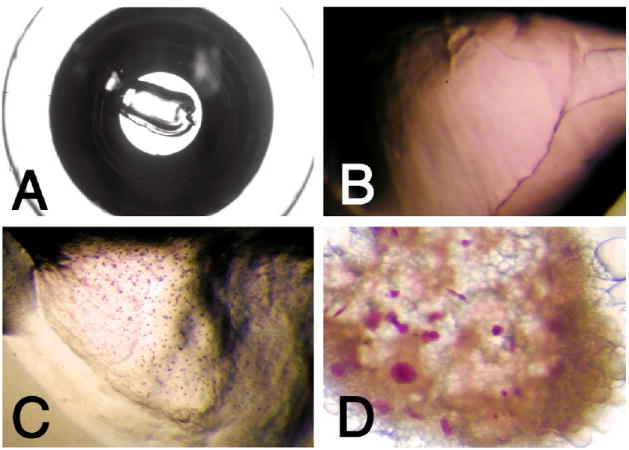
Growth of bacteriorhodopsin crystals using the syringe and microwell-based crystallization procedure. Shown are photographs of cubic phase crystallization setups in a microwell of a Terasaki plate. (A) Overview of well containing 0.2 μl cubic phase dispensed with manual syringe dispenser. Well bottom diameter is ca. 1.2 mm. (B) Close-up view of crystallization setup prior to crystallization. The purple bacteriorhodopsin is homogeneously distributed in the lipidic cubic phase. (C) Bacteriorhodopsin microcrystals formed in 0.2 μl of cubic phase when solid salt was used as a crystallization-inducing agent. (D) Purple bacteriorhodopsin crystals with sizes up to ca. 75 μm along the longest dimension were grown by adding 0.2 μl of initial monoolein cubic phase containing 3.5 mg/ml bacteriorhodopsin to 1 μl of 27% PEG 2000 in 100 mM Sørensen phosphate buffer, pH 5.6.
