Figure 2. Tissue distribution of drug nanoparticles after uptake by circulating monocytes.
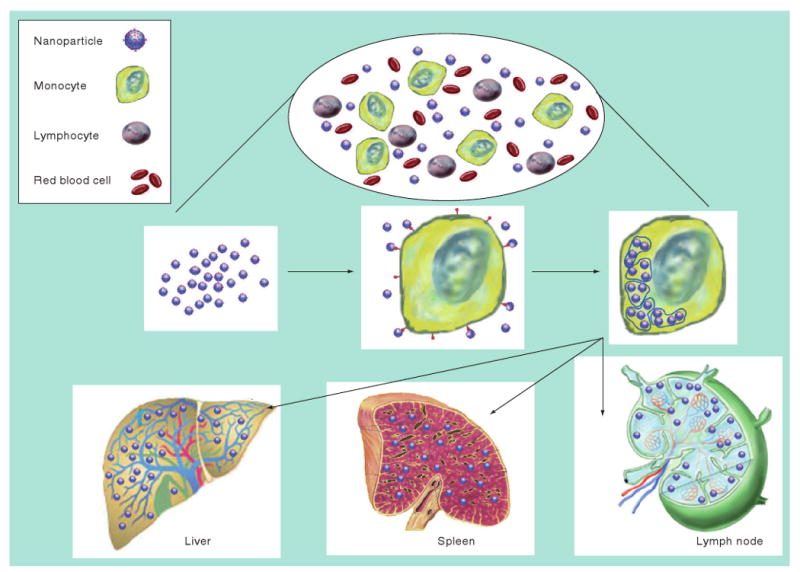
While in the blood (top), circulating immunocytes will specifically engulf nanoparticles by receptor-mediated endocytosis and store them within cytoplasmic vesicles (middle). The drug-laden cells will then respond to secreted chemokine messages and migrate from the circulation by diapedesis through vascular epithelial cells into target organs or travel through the reticuloendothelial system (bottom). The drugs are then released slowly ensuring that therapeutic concentrations are maintained for extended time periods.
