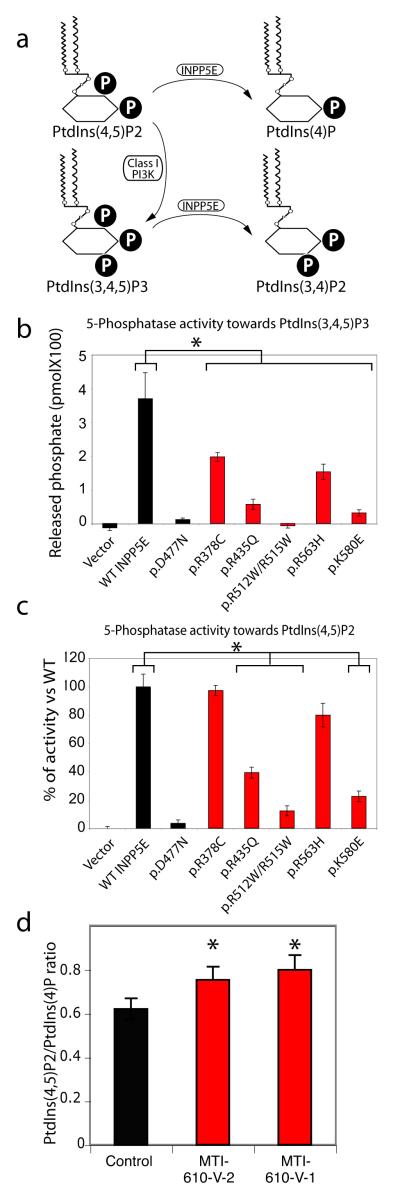
Figure 2.
Impaired 5-phosphatase activity and altered ratio of PtdIns(4,5)P2 to PtdIns(4)P associated with JBTS1 INPP5E mutations. (a) Summary of PtdIns metabolism. P = phosphate. A block in INPP5E function is predicted to increase the PtdIns(4,5)P2:PtdIns(4)P ratio. (b-c) More severe reduction in 5-phosphatase activity of mutant INPP5E against PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 than PtdIns(4,5)P2 substrates. Note that activity was largely retained against PtdIns(4,5)2 for some mutations (mutants R435Q, R512W/R515W and K580E are severely defective, whereas R378C and R563H are only slightly diminished). D477N is known phosphatasedead, compared with each of the patient mutations. (N = 3 for each sample) (d) Elevated ratio of PtdIns(4,5)P2 to PtdIns(4)P in patient primary fibroblast lines MTI-610-V-2 and V-1, compared with control fibroblast. * represent p < 0.05 ANOVA two way corrected for multiple comparisons.