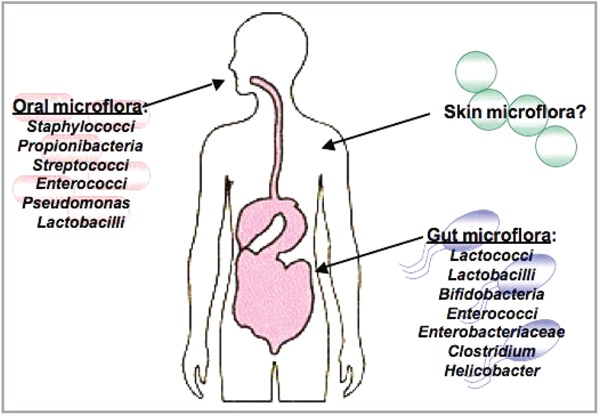
Fig 1.
Resident microflora that are beneficial to the host. The gut and mouth contain many species of microflora. Microbiota in the intestines protect the host by educating the immune system and preventing pathogenic infections. These microflora benefit the systemic immune system of the host and positively affect other organs, such as the lung. In the mouth, over 500 species of bacteria protect the mucosa from infections by preventing colonization of dangerous yeasts and other bacteria. It is yet unclear if the microflora of the skin play a similar role in protecting the host. Image from http://www.giconsults.com with permission.