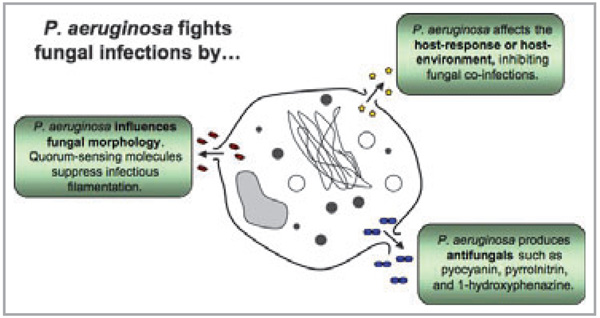
Fig 5.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa fights fungal infections. It produces compounds such as pyocyanin, pyrrolnitrin and 1-hydroxyphenazine which kill and inhibit fungal growth. Pseudomonas aeruginosa also prevents the morphological transition of fungi from yeast-form cells to virulent filamentous cells. Filamentation of Candida albicans is associated with pathogenesis, adhesion, invasion and virulence-related products. Pseudomonas aeruginosa interacts with the host creating an environment inhospitable to fungi.