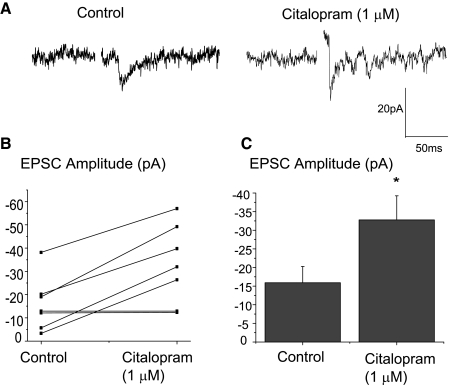
FIG. 4.
Application of the serotonin (5-HT) reuptake inhibitor citalopram (1 μM) significantly increased the peak amplitude of the excitatory synaptic response in cardiac vagal neurons. A typical experiment is illustrated in the top traces, A, and the summary results from 7 experiments are shown in B and C. Citalopram (1 μM) increased the responses evoked by the stimulation of trigeminal afferents by an average of 106.2 ± 6.9% from −15.9 ± 4.4 to −32.8 ± 6.5 pA (n = 7, P < 0.05).