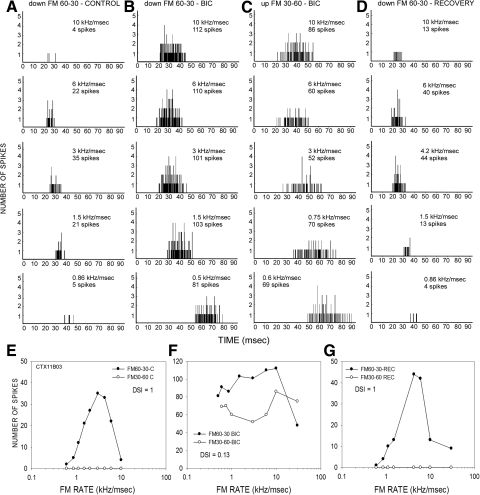
FIG. 2.
A neuron in which BIC eliminated direction selectivity in the auditory cortex. A: poststimulus time histographs (PSTHs) showing the responses to downward FM sweep (60–30 kHz) at different sweep rates. B and C: PSTHs of response to downward (B) and upward (C) sweeps in the presence of BIC (20 nA ejection current). D: PSTHs of responses to downward FM sweeps in the recovery condition. E: in the control condition, this neuron responded to a 60 to 30 kHz downward sweep, but not to a 30 to 60 kHz upward sweep (DSI = 1). F: injection of BIC caused an increase in response magnitude for both up- and downward sweeps (note different scales on y axis compared with E). The responses to upward sweeps were increased at all sweep rates. The DSI in the presence of the antagonist was 0.13, indicating a considerable decrease in direction selectivity. G: control DSI was recovered ∼15 min after the ejection current was turned off.