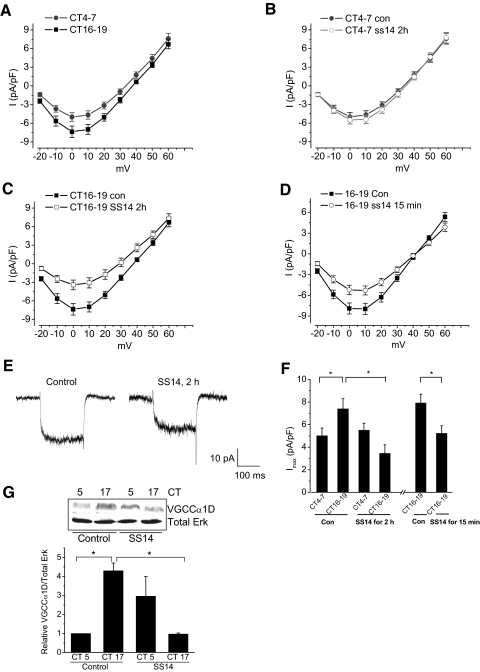
FIG. 1.
There is a circadian phase-dependent modulation of cone L-type voltage-gated calcium channels (L-VGCCs) by somatostain-14 (SS14). The current density-voltage (I-V) relationship was obtained from whole cell recordings on the 2nd day of constant darkness (DD). A: the L-VGCC currents were larger during the subjective night [circadian time (CT) 16–19; solid square] than during the subjective day (CT 4–7; solid circle). B: treatment with SS14 (500 nM) for 2 h prior to recordings (○) did not have significant effects on the current density during the day. C: treatment with SS14 for 2 h (□) significantly decreased the L-VGCC current density during the night compared with the control (▪). D: treatment with SS14 for 15 min prior to recordings (○) significantly inhibited the L-VGCCs during the subjective night. E: 2 representative traces recorded during the subjective night from the control (con) and SS14-treated (SS14 2h) groups show currents elicited from −65 to 0 mV. The maximum currents were obtained when the steps depolarized to 0 ∼10 mV. F: treatment with SS14 for 2 h or 15 min prior to recordings significantly decreased the maximum L-VGCC current density (Imax) elicited from −65 to 0 mV during the subjective night. The maximum current density of voltage step to 0 mV: control CT 4–7 (con CT 4–7): 5.0 ± 0.7 pA/pF, n = 24; control CT 16–19 (con CT 16–19): 7.4 ± 0.9 pA/pF, n = 21; treatment with SS14 for 2 h (SS14 for 2 h) CT 4–7: 5.5 ± 0.6 pA/pF, n = 26; SS14 for 2 h CT 16–19:3.4 ± 0.8 pA/pF, n = 26; treatment for 15 min control (con) CT 16–19: 7.9 ± 0.8 pA/pF, n = 14; treatment with SS14 for 15 min (SS14 for 15 min) CT 16–19: 5.2 ± 0.7 pA/pF, n = 15, * P < 0.05. G: the protein levels of L-VGCCα1D in cultures harvested during the subjective night (CT 17) were significantly higher than during the subjective day (CT 5) in controls. Treatment with SS14 (500 nM) for 2 h significantly decreased the L-VGCCα1D during the subjective night, *, P < 0.05.