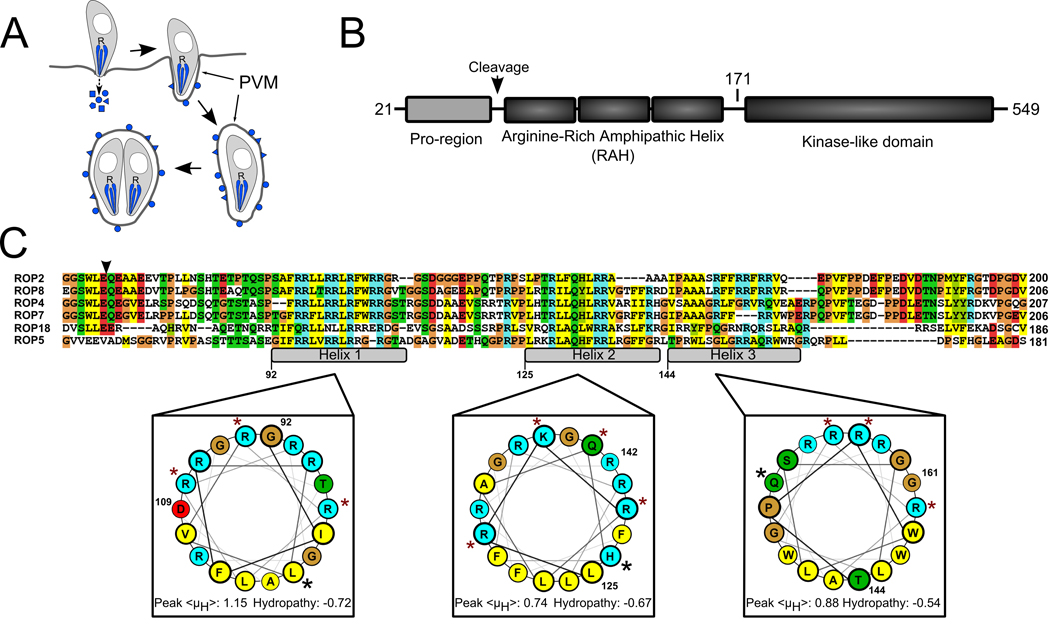
Figure 1. The ROP2-family domain architecture.
A) During Toxoplasma invasion of a host cell, its rhoptries (R) secrete their contents of effector molecules (blue) into the host cytosol. Many of these molecules associate with the PVM, which expands as the parasite replicates inside. B) Members of the ROP2-family have three domains following their signal peptides: a pro-region that is proteolytically processed in all members except for ROP5, a series of three arginine-rich amphipathic helices (RAH domain) and a protein kinase-like domain that appears to be catalytically inactive in all family members except for ROP18. Numbering is according to ROP5. The schematic is not drawn to scale. C) The RAH domain is the region of highest identity among the various family members. The putative processing site that precedes the RAH is marked with an arrowhead. The three amphipathic helices are marked in the alignment and numbered according to the ROP5 sequence. The ROP5 helices are projected on helical wheels and the average hydropathy and peak hydrophobic moment, <μH>, of each is shown, calculated according to the Eisenberg consensus scale (27). Blue shading indicates basic residues, red indicates acidic residues, yellow indicates hydrophobic residues, green indicates polar, and glycines and prolines are shaded tan. Residues that have been mutated to glutamate in the present study are marked with a red star. Residues that have been mutated to proline are marked with a black star.