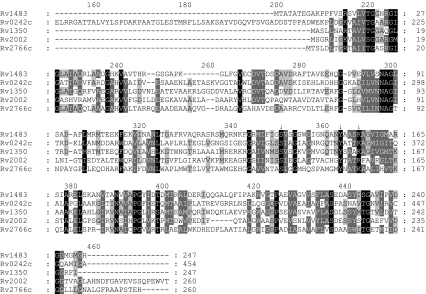
Fig. 1.
Homology study of M. tuberculosis FabG proteins. Multalin- and Genedoc-based comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence of FabG1 (Rv1483) with those of its homologs FabG2 (Rv1350), FabG3 (Rv2002), FabG4 (Rv0242c) and FabG5 (Rv2766c). Dashes indicate the arrangement of the sequences for best fit, and arrows point to the amino acids forming the catalytic triad (Marrakchi et al. 2002). The first 150 amino acid residues of FabG4 do not match any of those of the other homologs, and were removed from the figure. Black shadings refer to strictly conserved amino acid residues among all the sequences, whereas the darker and lighter grayshadings denote regions with more relaxed residue similarities not necessarily shared by the full set of sequences