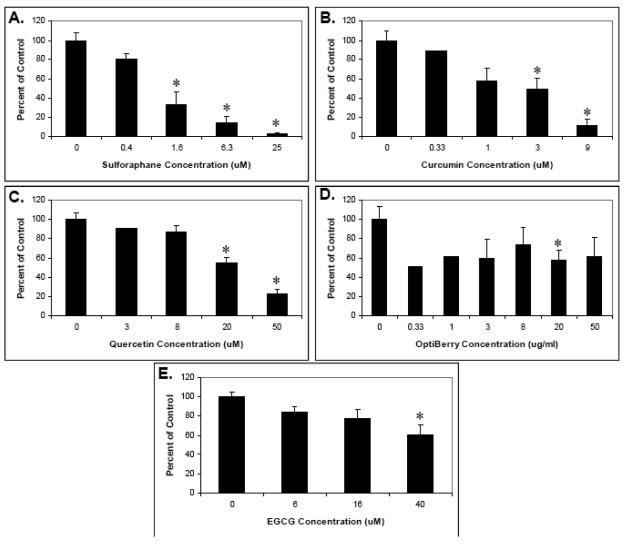
Fig. 1. Human T-lymphocyte suppression by select phytochemicals.
Human T-lymphocytes were isolated, pretreated with the indicated phytochemical supplements at various concentrations for 30 minutes, and stimulated with 5 ug/ml each of soluble anti-human CD3 plus anti-human CD28. Proliferation was then measured by tritiated thymidine incorporation. (A) Sulforaphane. (B) Curcumin. (C). Quercetin. (D) Berry extracts (E) EGCG. Data is expressed as means +/− SEM (N=3-5). For data points without error bars, N=2. Statistically significant differences between control and treated samples were assessed by the Kruskal-Wallis test. *P < .05.