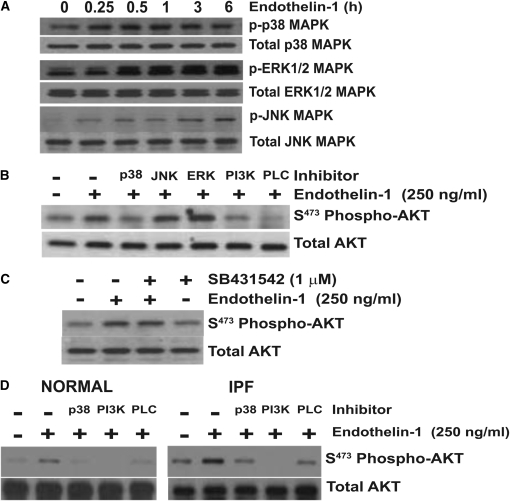
Figure 2.
AKT phosphorylation by ET-1 requires p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). (A) Quiescent IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with ET-1 (250 ng/ml) for the time periods indicated. Whole-cell lysates were assessed by SDS-PAGE immunoelectrophoresis and Western immunoblotting for: phospho p38 MAPK, phospho extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 MAPK, and phospho JNK MAPK. Membranes were stripped and probed for the corresponding total MAPK. (B) IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with ET-1 (250 ng/ml) for 3 hours in the presence/absence of inhibitors of p38 MAPK (SB203580, 6 μM), JNK MAPK (SP600125, 100 nM), ERK1/2 (PD98059, 20 μM), PI3K (Wortmannin 50 nM), or PLC (U73122, 5 μM). Whole-cell lysates were assessed for AKT phosphorylation by Western immunoblotting, and the membrane was stripped and probed for total AKT. (C) IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with ET-1 (250 ng/ml) in the presence/absence of SB431542 (1 μM), an inhibitor of the type-1 TGF-β receptor (ALK5). Cell lysates obtained at 3 hours were assessed for AKT phosphorylation by Western immunoblotting, and the membrane was stripped and probed for total AKT. (D) Primary normal adult lung fibroblasts (left panel) and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) fibroblasts (right panel) were treated with ET-1 (250 ng/ml) for 3 hours in the presence/absence of inhibitors of p38 MAPK (SB203580, 6 μM), PI3K (Wortmannin 50 nM), or PLC (U73122, 5 μM). AKT phosphorylation was assessed by Western immunoblotting, and membranes were stripped and probed for total AKT. Data represent three normal and three IPF fibroblast cell lines.