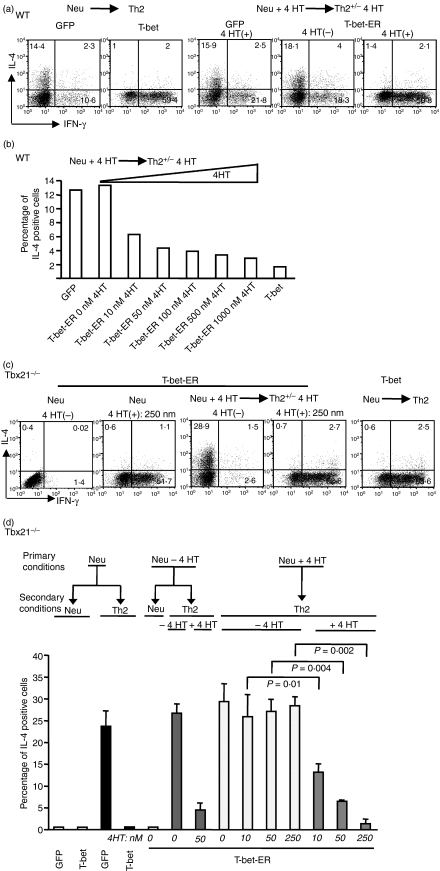
Figure 4.
Continuous T-bet expression is required to silence the interleukin-4 (IL-4)-producing potential in T helper type 1 (Th1) cells. (a) Naïve CD4+ T cells of wild-type (WT) mice were stimulated under the neutralized conditions and infected with green fluorescent protein (GFP), T-bet or a T-bet-oestrogen receptor fusion molecule (T-bet-ER) retrovirus. The GFP- and T-bet-infected cells were cultured for 9 days before they underwent Th2-inducing conditions for a period of 5 days. The GFP- and T-bet-ER-infected cells were cultured in the presence of 50 nm 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4HT) for 9 days before they were reprimed under Th2 conditions in the absence or presence of 50 nm of 4HT. Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and IL-4 expression were measured by intracellular staining and GFP+ cells are shown. (b) Naïve CD4+ T cells were used and the priming and repriming conditions were the same as those described in (a) except for the doses of 4HT. The percentages of IL-4-positive cells in the infected cells (GFP+ cells) are shown. (c,d) Naïve CD4+ T cells from Tbx21−/− mice were stimulated and infected with GFP, T-bet or T-bet-ER retrovirus. The T-bet-ER-infected cells were then cultured in the absence or presence of different doses of 4HT as indicated for 9 days. The resultant cells were then reprimed under Th2 conditions. The 4HT treatments in the secondary priming conditions are indicated. The percentages of IL-4-positive cells in the infected cells (GFP+ cells) are shown. The error bars represent the standard deviation derived from triplicate measurements. The presented data are representative of three independent experiments.