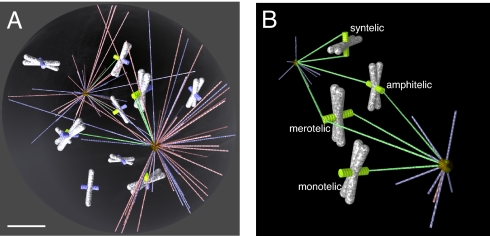
Fig. 1.
Computer model of spindle assembly. (A) MTs (growing in blue, shortening in red, captured in green) searching from two foci (centrosomes) for KTs (captured in green, not captured in blue) on the chromosomes (white/gray). (Scale bar, 2 mm.) (B) Four possible types of chromosome attachments. Amphitelic attachment: The two sister KTs are bound to MTs coming from opposite poles. Monotelic attachment: One sister KT is bound to MTs, whereas the other is unattached. Syntelic attachment: Both sister KTs are bound to MTs from the same spindle pole. Merotelic attachment: One KT is bound to MTs from opposite spindle poles.