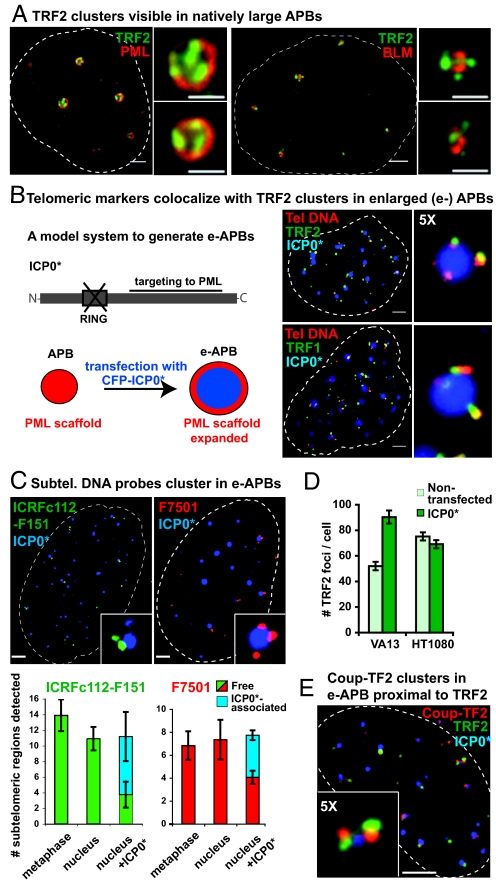
Fig. 1.
Chromosome ends associate with PML bodies to form APBs in VA13 cells. (A) Individual telomeres as detected by anti-TRF2 antibody (green) may appear associated with the surface of naturally large APBs, revealed here by either anti-PML or anti-BLM antibodies (both red). (B) Viral protein ICP0 lacking the ring finger domain fused to CFP (CFP-ICP0*, blue) was used to transiently enlarge the size of APBs (hereafter e-APBs). In e-APBs, telomeric DNA detected by PNA FISH (red) colocalizes with either TRF2 or with TRF1 protein foci (green). (C) Subtelomeric probes ICRFc112-F151 (green) and F7501 (red), cluster in e-APBs containing CFP-ICP0* (blue). These probes detect only a specific subset of chromosome arms (Fig. S3A). Histograms showing the average number of subtelomeric regions detected in 20 metaphase spreads, cell nuclei, and nuclei containing ICP0*. ICP0* associated, subtelomeric signals in proximity of ICP0*; Free, elsewhere in the nucleus. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). (D) Histogram showing the average number of TRF2 foci expected and actually detected in interphase nuclei of native and ICP0*-transfected VA13 and HT1080 cells. Error bars, SEM. (E) Coup-TF2 is localized in close proximity of TRF2 clusters in e-APBs. (Scale bars, 2 μm and 1 μm in enlarged images.)