Fig. 1.
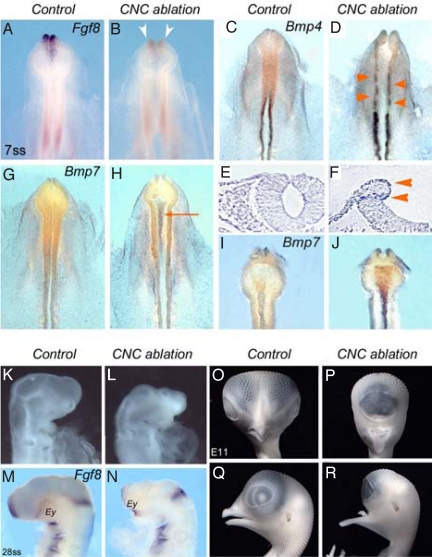
Expression Fgf8 and Bmps at 7 ss following the ablation of CNC at 5 to 6 ss. (A and B) Fgf8 activation in ANR of 7-ss control embryo (A) is lost in CNC-ablated embryo (B; arrowheads). (C-F) Bmp4, which is normally no longer expressed in the anterior CNC at 7 ss (C), is activated in the neuroepithelium underlying the excised CNC and up-regulated in the more caudal rhombencephalic CNC (D; arrowheads). (E and F) On a transverse section at the mesencephalic level, Bmp4 transcripts are present at the healing point where the ectoderm and neuroepithelium abut each other and at the hinge point where the neuroepithelium folds (F; arrowheads; compare with control in E). (G-J) At 7 ss, Bmp7 transcripts are slightly accumulated in the Pcp in control (G and I), whereas in CNC-ablated embryos (H; arrow), Bmp7 expression is considerably increased in Pcp and notochord, as evidenced on the ventral side after dissection (J). (K-R) Effect of Bmp7 on brain development. (K) Normal head development at E2.5. Injection of Bmp7 results in the inhibition of pre-otic brain development (L), the down-regulation of Fgf8 in ANR (N), and the convergence of eye fields (Ey; compare with control in M). (O-R) Gross anatomy of control (O and Q) and Bmp7-supplemented (P and R) embryos at E11. (M and N) These alterations result in long-term reduction of forebrain morphogenesis, cyclopia, and agenesis of naso-frontal structures, whereas the mandibular ones are not affected (Q and R).