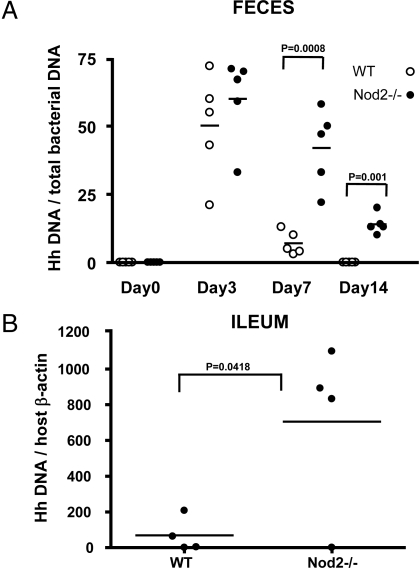
Fig. 4.
Nod2 suppresses colonization of pathogenic commensal bacteria in the terminal ileum. (A) H. hepaticus (5 × 108/mouse) was inoculated into wild-type and Nod2-deficient mice via gastric gavage. Fresh feces samples were collected from mice at 0, 3, 7, and 14 days after inoculation, and DNA was purified. H. hepaticus colonization was quantified by real-time PCR using H. hepaticus-specific primers and 100 ng of purified DNA per reaction. Data were normalized by real-time PCR data for Eubacteria using the bacteria 16S RNA gene primer sets, which detect all bacterial strains. The p-values were determined by Student's t test. (B) Terminal ilea were isolated from wild-type and Nod2-deficient mice, and DNA samples were prepared. H. hepaticus colonization was quantified by real-time PCR using H. hepaticus-specific primers and 100 ng of purified DNA per reaction. Data were normalized by real-time PCR data for the β-actin gene in host genomic DNA. The p-values were determined by Student's t test.