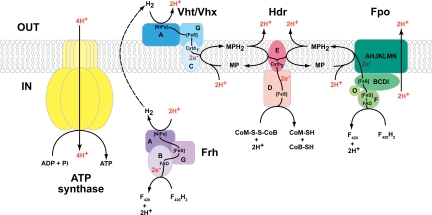
Fig. 1.
The electron transport chain of M. barkeri has been proposed to comprise 2 energy-conserving systems, the F420H2:heterodisulfide oxidoreductase and the H2:heterodisulfide oxidoreductase. In the former system, F420H2 is oxidized by FpoF releasing 2 electrons that are transferred through FpoBCDI and then FpoAHJKLMN to membrane-soluble methanophenazine. This reaction is coupled to the pumping of 2 protons outside the cell. Reduction of methanophenazine consumes 2 protons from the cytoplasm, which subsequently are released outside the cell upon oxidation of MPH2. The electrons then are transferred through HdrED to reduce CoM-S-S-CoB with 2 protons from the cytoplasm. Alternatively, in the H2:heterodisulfide oxidoreductase, H2 is oxidized by Vht/Vhx to produce 2 protons outside the cell and 2 electrons that are transferred to MPH2, which then is used to reduce CoM-S-S-CoB. The dashed arrow represents a third possible energy-conserving mechanism that is proposed in this study. In this pathway, F420H2 is oxidized by the cytoplasmic hydrogenase Frh to generate H2. The H2 then diffuses outside the cell to the active site of membrane-bound hydrogenase Vht/Vhx, where it is reoxidized, resulting in the translocation of 2 protons via a H2-cycling mechanism. The electrons are passed through methanophenazine to CoM-S-S-CoB, as in the other 2 systems. In all 3 systems, the entire electron transport process leads to the net translocation of 4 protons (highlighted in red) outside the cell per 2 electrons transferred from F420H2 or H2 to the CoM-S-S-CoB. The electrochemical gradient generated is coupled to ATP synthesis via an A-type ATPase. Abbreviations: CoB-SH, coenzyme B; CoM-SH, coenzyme M; CoM-S-S-CoB, mixed disulfide of CoM-SH and CoB-SH; Cytb2, cytochrome b2; F420/F420H2, oxidized and reduced Factor 420; FAD, flavin adenine dinucleotide; [FeS], iron-sulfur cluster; Fpo, F420H2:phenazine oxidoreductase; Frh, F420-reducing hydrogenase; Hdr, heterodisulfide reductase; MP/MPH2, oxidized and reduced methanophenazine; [NiFe], bimetallic catalytic center; Vht/Vhx, methanophenazine-dependent hydrogenase.