Figure 3. In vitro generation of IFN-inducing RNA requires ATP and UTP.
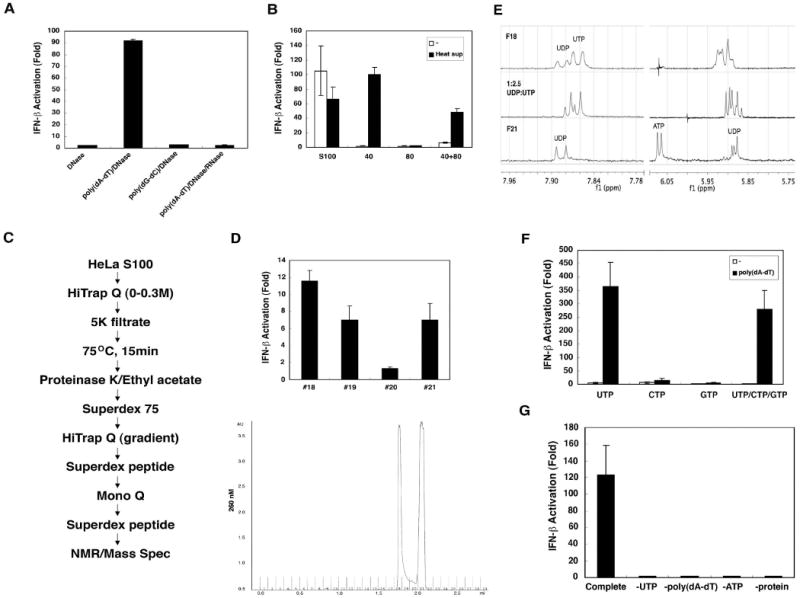
(A) HeLa S100 was incubated with poly(dA-dT) or poly(dG-dC) (20 μg/ml) and ATP (2mM) at 30°C for 1 hour. RNA was extracted with phenol/chloroform after DNase I (0.2 U/μl) and/or RNase A (0.1mg/ml) treatment, then transfected into HEK293-IFNβ-luciferase reporter cells. (B) HeLa S100 was precipitated with 40% ammonium sulfate, then the supernatant was further precipitated with 80% ammonium sulfate. The precipitates were dialyzed and incubated with poly(dA-dT) and ATP in the presence or absence of the supernatant from heat-treated HeLa S100 (“heat sup”). RNA from the in vitro reaction was extracted and transfected into HEK293-IFNβ-luciferase reporter cells. (C) Scheme of purification of heat-resistant factor required for the generation of IFN-inducing RNA. (D) Chromatogram (A260) of the small molecules on Superdex peptide column (last step; lower panel). Factions from the Superdex peptide column were incubated with a protein fraction from 40% ammonium sulfate precipitation, poly(dA-dT) and ATP, and then the RNA were extracted for IFN-β reporter assays (upper panel). (E) NMR spectra of fractions 18 (F18; top spectrum) and 21 (F21; bottom). The middle spectrum is a mixture of authentic UDP and UTP standards (1:2.5). (F) UTP, CTP, GTP or UTP/CTP/GTP (1.5 mM) was used to substitute for the “heat sup” in the in vitro reaction, and then RNA was extracted for IFN-β reporter assays. (G) Reactions containing a crude protein fraction (40% ammonium sulfate precipitate), poly(dA-dT), ATP and UTP (complete reaction) or lacking one of the components as indicated were carried out in vitro, and then RNA was extracted for IFN-β reporter assays.
