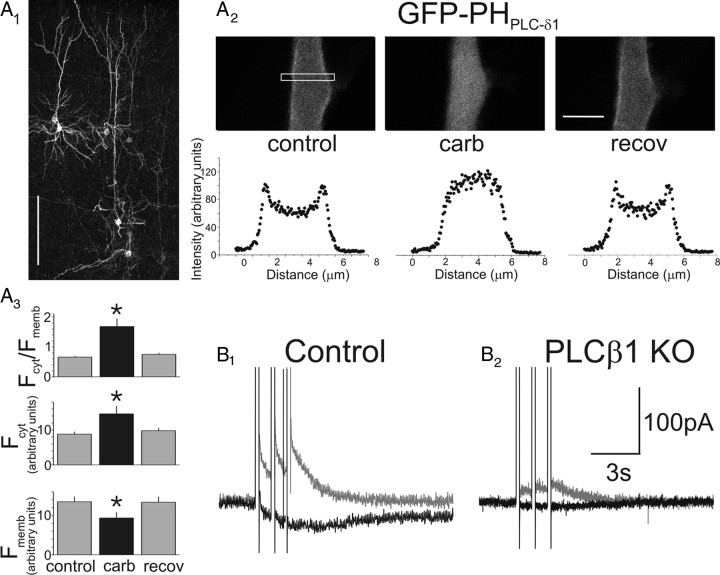
Figure 3.
Muscarinic receptors elicit the breakdown of PtdIns(4,5)P2 in pyramidal cells and signal IsADP through PLCβ1. A1, Flattened confocal image stack illustrating a group of cortical pyramidal cells in an organotypic brain slice transfected with GFP–PHPLCδ1. Scale bar, 200 μm. A2, Top, Close up of the proximal apical dendrite of a pyramidal cell transfected with GFP–PHPLCδ1 at rest (left), in the presence of carbachol (middle), or after recovery from the agonist (right). Notice the redistribution of GFP–PHPLCδ1 away from the membrane during the application of carbachol. Scale bar, 5 μm. Bottom, Quantification of the redistribution of the fluorescent reporter in the top during administration of carbachol. The region sampled for these plots is denoted by a box in the left top. A3, Graph summarizing the changes in GFP–PHPLCδ1 fluorescence at the membrane (Fmemb) and in the cytosol (Fcyt) during carbachol administration. n = 6 cells; *p < 0.05. B1, Administration of carbachol (30 μm) to a prefrontal cortex pyramidal neuron in a slice derived from a wild-type mouse induces IsADP. B2, In contrast, administration of carbachol to a pyramidal cell derived from PLCβ1 knock-out mice fails to induce IsADP under the same experimental conditions. The difference in IAHP between the cells illustrated here is within the range of cell-to-cell variability expected for slow and medium afterhyperpolarization currents in pyramidal cells of prefrontal cortex (Villalobos et al., 2004).