Figure 7.
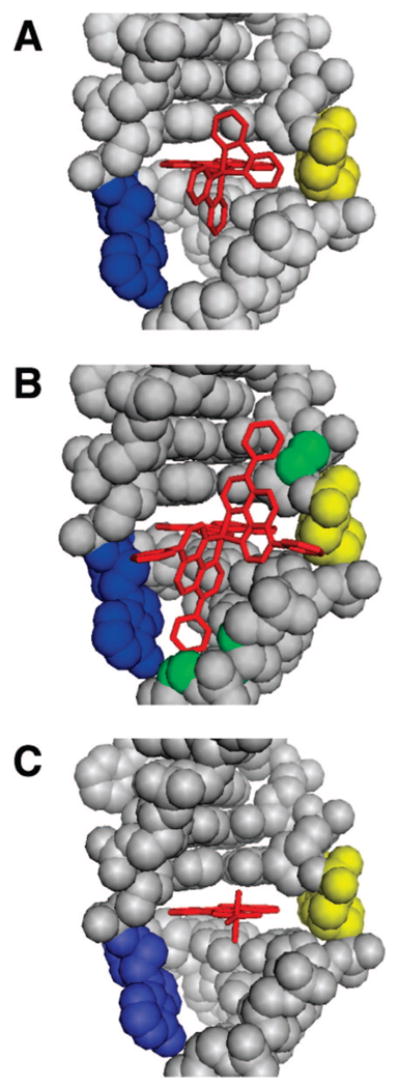
Crystal and model structures of rhodium metalloinsertors bound to the mismatch site. Rhodium insertors (red) are shown bound to the DNA (gray) from the minor groove at the mismatch site with the bases (adenine in blue, cytosine in yellow) ejected and the chrysi ligand stacked fully with the adjacent base pairs. The crystal structure of Δ-Rh(bpy)2chrysi3+ bound to the CA mismatch is shown in panel (A), along with structural models of Δ-Rh(DIP)2chrysi3+ (B) and Δ-Rh(NH3)4chrysi3+ (C) binding based on the crystal structure. Superposition of the DIP complex upon the rhodium center of the bpy complex leads to steric clashes with the sugar–phosphate backbone (possible atoms involved in green), whereas the tetraammine complex is easily accommodated.
