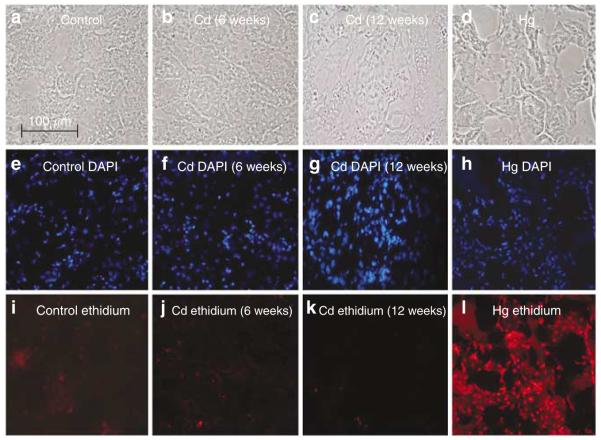
Figure 6. The effects of Cd and Hg on renal cell membrane integrity.
Animals were treated with either Cd (0.6 mg/kg, subcutaneously 5 days a week for 6 weeks) or HgCl2 (3.5 mg/kg of Hg, intraperitoneally), and the left kidneys were perfused with ethidium homodimer. Cryosections of the kidneys were then fixed, permeabilized, and labeled with DAPI to identify total nuclei. (a-d) Phase-contrast images corresponding to DAPI-labeled panels (e-h) and ethidium homodimer-labeled panels (i-l). No differences in ethidium homodimer labeling were detected in (j) 6-week Cd2+-treated samples or (k) 12-week Cd-treated samples compared with (i)12 week saline-treated control. In contrast, samples from Hg-treated animals showed widespread necrosis (l), as indicated by intense ethidium labeling (original magnification × 164).