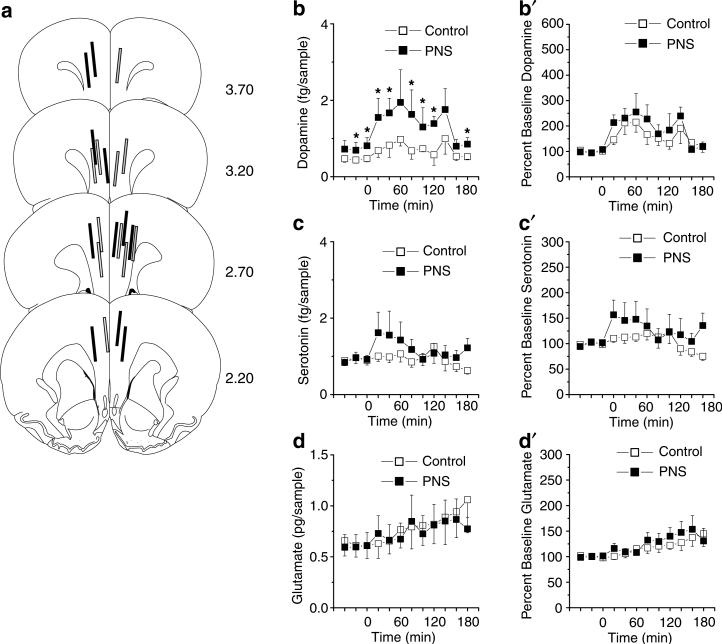
Figure 8.
Basal and cocaine-stimulated (15 mg/kg, i.p.) neurotransmitter levels in the PFC in PNS (for dopamine, n = 11 comprised one to three rats from six litters; for serotonin and glutamate, n = 10 comprised one to two rats from six litters) and control (for dopamine, n = 11 comprised one to three rats from five litters; for serotonin and glutamate, n = 10 comprised one to three rats from five litters) rats following a history of cocaine self-administration. (a) Summary of the PFC placements of the active membrane of the microdialysis probes of PNS (solid lines) and control (gray-filled lines) rats. (b–d) Absolute levels of dopamine, serotonin, and glutamate in the PFC before and after a cocaine challenge. (b′ and d′) Changes from baseline in PFC dopamine, serotonin, and glutamate levels following a cocaine challenge; data shown as mean±SEM transformed to percent change from the basal levels derived from the average of the final three prechallenge samples. Symbol indicates a significant difference between the PNS and control rats (*p<0.05).