Figure 1. Cytoskeletal filaments.
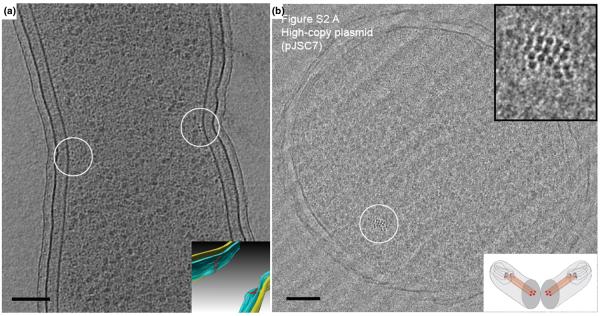
(A) 8-nm tomographic slice of a dividing Caulobacter crescentus cell, showing the filaments in cross-section (small dark dots near the center of the circles). Since the reconstruction can be visualized in 3-D, these filaments can be segmented (Inset). Filaments (red), outer membrane (yellow), and inner membrane (blue). Scale bar 100 nm. Adapted from [5] with permission from Nature Publishing Group. (B) Vitreous cryo-section of an E. coli cell carrying a high-copy ParMRC-bearing plasmid. The nominal thickness of the section is 50 nm. A bundle of filaments are shown in the circle. Top inset: enlarged view. Bottom inset: illustration showing the cellular plane (grey) seen in the image. Scale bar 100 nm. Adapted from [11] with permission from the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
