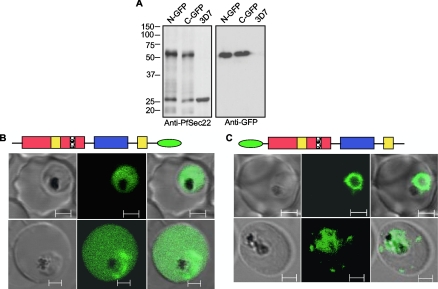
FIG. 4.
Live-cell imaging of GFP-tagged PfSec22 chimeras. (A) Immunoblot analyses using anti-PfSec22 antibodies (left blot) or monoclonal anti-GFP antibodies (right blot) confirmed expression of the N-terminal GFP-tagged PfSec22 (N-GFP) and the C-terminal GFP-tagged PfSec22 (C-GFP) proteins (∼54 kDa) in the respective transgenic cell lines, but not in untransfected parasites (3D7). The anti-PfSec22 antibodies also detected an ∼26-kDa protein that corresponded to the untagged PfSec22 protein in whole-cell extracts from all three cell lines. (B) Live-cell imaging of parasites expressing the C-terminal GFP-tagged PfSec22 (PfSec22-GFP) showing diffuse localization of the protein throughout the parasite cytoplasm and occasionally in the host cell compartment. (C) Confocal micrographs showing localization of the N-terminal GFP-tagged protein (GFP-PfSec22) in early- trophozoite (top row) and mid-trophozoite (bottom row) stage parasites. In addition to the ER-like profiles, GFP-PfSec22 associates with tubovesicular elements in the infected host cell. The micrographs (left to right) represent differential interference contrast, GFP fluorescence, and a merge of the two. Scale bars, 2 μm.