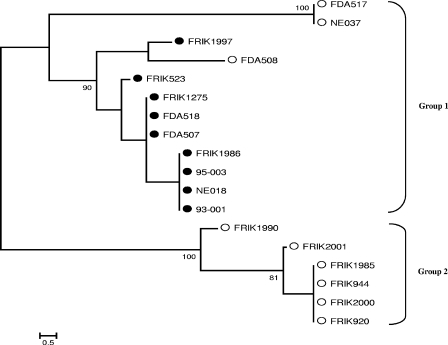
FIG. 1.
Unrooted neighbor-joining tree of the 18 lineage strains, based upon the number of differences in parsimony-informative sites among rhsA, -C, -D, -E, -F, -J, and -K. SNPs identified in each rhs gene (Table 3) were concatenated to represent the SNP sequence type for each O157:H7 strain. Parsimony-informative sites were used to construct the phylogenetic tree. Since sequence information of rhsI was not available for all strains, rhsI was not included. Bootstrap values (1,000 replications) above 75 are shown at the interior branches. Substitutions per site are indicated by the bar at the bottom. The strains marked by open circles are lineage II strains, and strains marked by solid circles are lineage I strains, whose designations were defined previously by Kim et al. (22) and were confirmed in Table 4.