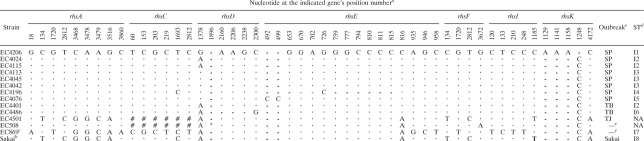
TABLE 2.
Sequence variations (SNPs, insertions and deletions) identified by in silico comparison of 7 rhs genes from 14 E. coli O157:H7 strains
SNP positions are based upon the corresponding rhs gene of the E. coli O157:H7 strain Sakai. Vertical numbers represent the nucleotide position of each SNP (i.e., the first column represents nucleotide position 18 of rhsA). Identical nucleotides at each SNP locus are indicated by dots. Gaps at each SNP locus are indicated by dashes. #, complete sequences of rhsC of EC4501 and EC508 were not found within the GenBank entries; *, there is an insertion from nucleotide positions 1896 to 1949 in rhsD of EC508.
Sequences of rhsD and rhsE for strain Sakai were obtained by sequencing in this study. Sequences of the other rhs genes for strain Sakai were extracted from GenBank (accession number BA000007) using Artemis (version 9) (37).
The first 101 nucleotides of rhsI from strain EC869 were missing.
I stands for in silico comparison; numbers were assigned to different STs.
SP stands for the 2006 spinach E. coli O157:H7 outbreak (10). TB stands for the 2006 Taco Bell E. coli O157:H7 outbreak (9). TJ stands for the 2006 Taco John E. coli O157:H7 outbreak (14). Sakai stands for E. coli O157:H7 strain Sakai (16). EC508 and EC869 are human fecal and USDA isolates, respectively (20), and are not associated with the aforementioned outbreaks.