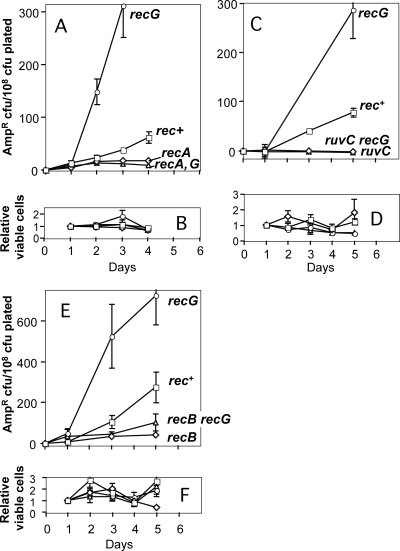
FIG. 1.
DSBR protein-dependent stationary-phase mutation to ampicillin resistance (Ampr) during prolonged starvation. (A, C, and E) Lac assay strains were starved on lactose medium for several days, and replicate plates were removed each day, overlaid with agar containing another carbon source and ampicillin, and reincubated to allow growth of Ampr mutant colonies. The data are the means ± standard errors of the means of six independent cultures per strain assayed in parallel. Each graph is representative of at least three repetitions. The days indicated are the days on which the ampicillin overlay was performed, and the data show the number of Ampr cells that were present on that day. The counts for day 0 (for the generation-dependent mutants present when the cultures were plated) were subtracted from the counts for stress-induced ampD mutants to more clearly show the increases in the numbers of mutants (when present) over time. Negative values were obtained when the average number of mutants from one set of replicate plates overlaid on a day was lower than the number of mutants for the set of plates overlaid on day 0. In all experiments, the rec+ strain (open squares) was SMR5222, and the recG strain (open circles) was SMR5578. (A) Ampr mutants accumulate during prolonged starvation on lactose. RecA is required for, and RecG inhibits, formation of these mutants. Open diamonds, recA strain SMR5225; open triangles, recA recG strain SMR5652. (C) Ampr stationary-phase mutation requires ruvC. Open diamonds, ruvC strain SMR6485; open triangles, ruvC recG strain SMR6927. (E) Ampr stationary-phase mutation requires recB. Open diamonds, recB strain SMR5228; open triangles, recB recG strain SMR6487. (B, D, and F) Daily levels of Lac− viable cells on the plates, normalized to the day 1 count, showing little net growth or death. For each panel the symbols are the same as those for the panel above it.