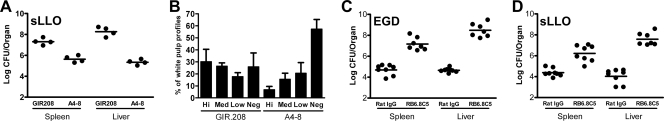
FIG. 7.
Characterization of sLLO strain infection in C.B-17 mice. (A and B) C.B-17 mice were treated with 1 mg of either the LLO-neutralizing antibody A4-8 or the GIR.208 control antibody, and 24 h later, they were infected with 108 CFU of the sLLO strain. (A) Mice were sacrificed at day 2 postinfection, and colony counts were determined. (B) Histology from the mice was scored for extent of apoptosis. Lesions were classified by size from negative (neg; negative/no apoptosis) through low (small apoptotic lesions; <25% white pulp profile apoptotic), medium (med; medium apoptotic lesions, 25 to50% white pulp profile apoptotic), and high (hi; large apoptotic lesions; >75% white pulp profile apoptotic). The data show the percentage of white pulp profiles from each mouse that fit each of the four categories. Bars are the mean ± standard error of the mean from four mice per group. (C and D) C.B-17 mice were treated with 250 μg of RB6-8C5 or rat immunoglobulin G (IgG) at days −3 and −1. At day 0, mice were infected with either 104 CFU of EGD or 107 CFU of the sLLO strain. At day 3, mice were sacrificed and colony counts were determined. Points represent individual titers per mouse organ. Bars are the mean ± standard error for two independent experiments with three or four mice per group.