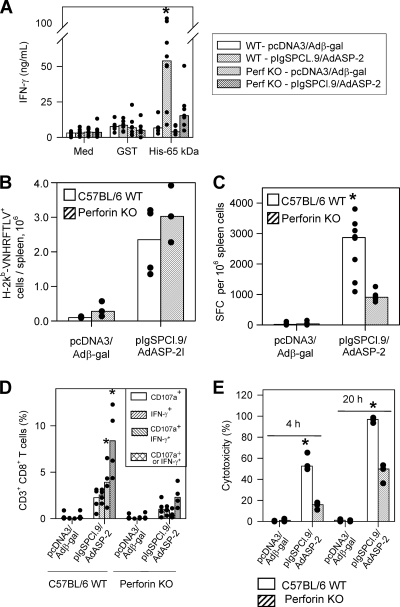
FIG. 4.
Cell mediated response of C57BL/6 WT or perforin KO mice after immunization with the heterologous prime-boost vaccination regimen. C57BL/6 WT or perforin KO mice were immunized as described in the legend of Fig. 3. Two weeks after the final immunizing dose, splenic cells were restimulated in vitro in the presence of medium (Med), recombinant glutathione S-transferase (GST; 10 μg/ml) or recombinant ASP-2 (His-65 kDa; 10 μg/ml [A]). When we compared all mouse groups, ASP-2-immunized WT spleens cells secreted more IFN-γ upon recombinant protein stimulation (asterisk, P < 0.05 in all cases). We estimated the frequency of specific splenic cells by staining with anti-CD8 and the multimer H-2Kb/VNHRFTLV (B) or the number of splenic IFN-γ spot-forming cells (SFC) by the ex vivo ELISPOT assay (C). When we compared groups of mice immunized with pIgSPCl.9/AdASP-2, immunized C57BL/6 WT mice had a higher frequency of SFC than the immunized perforin KO mice (asterisk, P < 0.001). Alternatively, these mice had their splenic cells cultured in the presence of anti-CD28 and FITC-labeled anti-CD107a, with or without the peptide VNHRFTLV. (D) After 12 h, cells were stained with APC-labeled anti-CD8, fixed, permeabilized, and stained with APC-Cy7-labeled anti-CD3, PE-Cy7-labeled anti-IFN-γ. When we compared groups of mice immunized with pIgSPCl.9/AdASP-2, immunized C57BL/6 WT mice had a higher frequency of CD3+CD8+ T cells expressing either IFN-γ or double-stained for CD107a/IFN-γ than the immunized perforin KO mice (asterisks, P < 0.01 in all cases). Finally, we estimated the in vivo cytotoxic activity by injecting immunized mice with CFSE-labeled splenic cells labeled with CFSE and coated with the peptide VNHRFTLV. (E) After 4 or 20 h, the in vivo cytotoxic activity was determined. When we compared groups of mice immunized with pIgSPCl.9/AdASP-2, immunized C57BL/6 WT mice displayed significantly higher in vivo cytotoxicity than perforin KO mice (asterisk, P < 0.01 in both cases). The results are expressed as medians (bars) and each individual mouse (dots) and are representative of experiments performed at least twice with similar results.