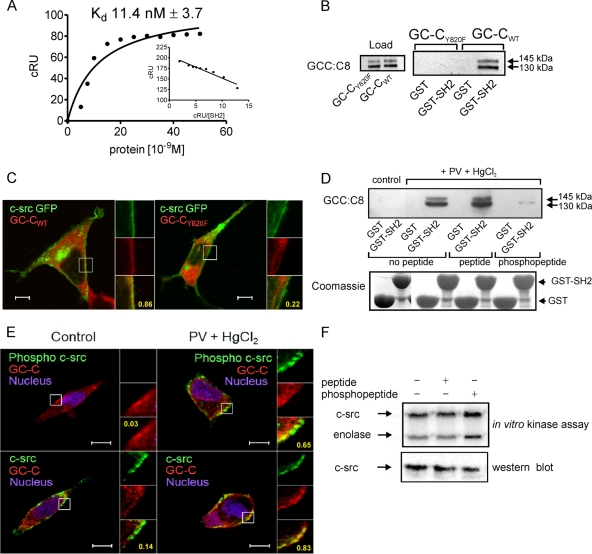
FIG. 4.
Interaction of GC-C with c-src via the SH2 domain contributes to colocalization of c-src and GC-C in the cell. (A) Surface plasmon resonance analysis of c-src SH2 binding to GC-C Y820 phosphopeptide. Inset, linear transformation of data. The data shown are from single sensogram with the experiment repeated twice. (B) GST-SH2 pulldown experiments were performed with lysates prepared from HEK293T cells transfected with either GC-CWT or GC-CY820F plasmid, along with a c-src plasmid. Proteins bound to the glutathione beads were analyzed by Western blotting with GCC:C8 monoclonal antibody. (C) Localization of GC-CWT or GC-CY820F with c-src GFP in HEK293T cells was observed using GCC:4D7 monoclonal antibody. Scale bar, 10 μm. Numbers indicate Pearson's coefficient for the region indicated in the box. The data shown are representative of experiments repeated thrice. (D) T84 cell lysates were allowed to interact with GST-SH2 in the presence of a peptide encompassing the Tyr820 residue or a peptide including a pY residue. Upper panel, Western blotting performed with GCC:C8 monoclonal antibody of proteins bound to beads. Lower panel, Coomassie blue-stained gel of GST and GST-SH2 proteins taken for pulldown experiments. (E) Immunofluorescence imaging was performed with T84 cells with phospho-c-src antibody and GCC:4D7 monoclonal antibody, or with c-src monoclonal antibody and a rabbit polyclonal antibody to GC-C, followed by incubation with anti-mouse Cy5 antibody and anti-rabbit Alexa 488 antibodies. Scale bar, 10 μm. Numbers indicate Pearson's coefficient for the region indicated in the box. The data shown are representative of experiments repeated thrice. (F) In vitro c-src kinase assay performed with c-src immunoprecipitated from HEK293T cells in the presence or absence of peptide or phosphopeptide. The lower panel shows a Western blot to detect the amount of c-src present in the immune complex used for the kinase assay.