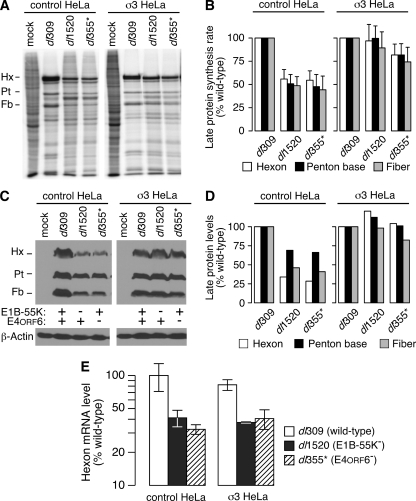
FIG. 6.
The reovirus σ3 protein corrects the defect in viral late protein synthesis during E1B-55K and E4orf6 mutant virus infections without restoring viral late mRNA transport. (A) CTRL-HeLa and σ3-HeLa cells were either mock infected or infected at an MOI of 10 PFU per cell with dl309, dl1520, or dl355*. At 36 h postinfection, cells were pulse-labeled for 1 h with radioactive amino acids. Protein from 104 cells was loaded per lane and separated by SDS-PAGE and then visualized by phosphorescence imaging. The image shown is representative of at least three experiments. The positions of the viral late proteins hexon (Hx), penton base (Pt), and fiber (Fb) are indicated to the left of the image. (B) The radioactivity present in the bands corresponding to hexon, penton, and fiber was quantified by phosphorimaging from three independent experiments and represents the rate of synthesis of each protein. Rates of synthesis during infection with wild-type virus were set to 100% for each cell line. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean. A two-tailed t test corrected for multiple comparisons indicates that the rates of synthesis during wild-type and mutant virus infections were significantly different in CTRL-HeLa cells (all P values were <0.03) but were indistinguishable in σ3-HeLa cells (all P values were >0.6). (C) Whole-cell lysates were collected at 36 h postinfection from CTRL-HeLa and σ3-HeLa cells that were mock infected or infected at an MOI of 10 PFU/cell with dl309, dl1520, or dl355*. Lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting for steady-state accumulation of the viral late proteins hexon, penton, and fiber by using antisera specific to the Ad5 virion. The level of β-actin protein is shown as a loading control. The immunoblot shown is representative of three experiments. (D) The total levels of hexon, penton, and fiber from the immunoblot shown in panel C were quantified by densitometry. The level of each protein in CTRL-HeLa or σ3-HeLa cells during the wild-type infection was set to 100%. (E) CTRL-HeLa and σ3-HeLa cells were infected at an MOI of 10 PFU/cell with dl309, dl1520, or dl355*, and cytoplasmic RNA was isolated at 36 h postinfection. Approximately 25 ng of purified RNA was reverse-transcribed to cDNA or incubated in the absence of reverse transcriptase and subsequently analyzed by quantitative PCR to measure the level of hexon mRNA. Cycle thresholds were compared to a standard curve generated using a titration of cytoplasmic RNA from wild-type virus-infected CTRL-HeLa cells that also underwent reverse transcription and quantitative PCR analysis. The value measured in CTRL-HeLa cells infected with wild-type virus was set to 100%. The data shown are representative of multiple experiments, and error bars represent the standard deviation between experiments. A two-tailed t test adjusted for multiple comparisons indicates there is significant variation between wild-type and mutant virus-infected cells (P < 0.005) and no difference among viruses between cell lines (P > 0.16). The results obtained in the absence of reverse transcriptase are not shown since the level of detection was negligible and generally more than 100-fold lower than the signal generated in its presence.