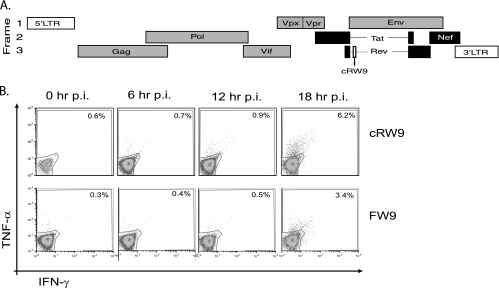
FIG. 1.
cRW9 is recognized at 18 h postinfection. cRW9 is located in frame with Rev (early) but in an ARF of Env (late). Early proteins (Tat, Rev, and Nef) are shown in black, while late proteins are shown in gray (A). LTR, long terminal repeat. We synchronously infected CD4+ T cells and used them in a kinetic recognition assay to determine when in the viral life cycle the cRW9 and Env-FW9 epitopes are recognized. Recognition was measured every 6 h as a percentage of cRW9-specific T cells that produce gamma interferon (IFN-γ) and/or tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) in response to recognition of infected cells. The top row represents recognition of MHC-matched, SIV-infected CD4+ T cells by cRW9-specific CD8-TL, while the bottom row represents recognition by Env-FW9-specific CD8-TL. No recognition was seen of MHC-mismatched cells at any time point. The viral life cycle is approximately 20 to 24 h, and both cRW9 and FW9 are recognized by 18 h after synchronous infection (B). Results are characteristic of at least three distinct experiments. p.i., postinfection.