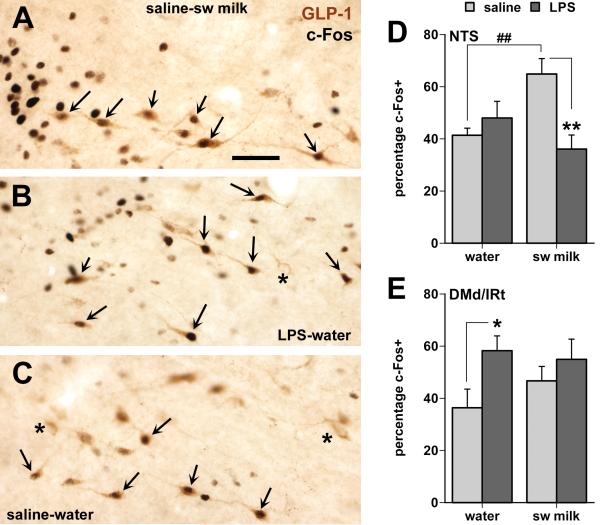
Fig. 5.
Effects of LPS treatment and sweetened milk consumption on c-Fos expression in GLP-1-immunoreactive neurons in the caudal NTS (A-D) and in those distributed within the dorsal and intermediate medullary reticular nuclei (DMd/IRt in E) in between the caudal-lateral NTS and the VLM. A-C: Photomicrographs of GLP-1 neurons in the NTS (situated just ventral to the tractus solitarius at the level of the caudal tip of the area postrema) many of which show black nuclear staining for c-Fos irrespective of treatment (arrows point at double-labeled cells, asterisks at GLP-1 neurons without c-Fos staining). Note that in the water-saline controls most of the c-Fos labeling in this region colocalizes with GLP-1 neurons (C), whereas many c-Fos nuclei in the sweetened milk (A) and LPS groups (B) are also present in neurons other than the GLP-1-labeled cells. Scale bar = 50 μm. D: Only the unrestricted consumption of sweetened milk by the saline-treated rats increased c-Fos expression in the GLP-1 neurons of the caudal NTS (##, ** p < 0.01). E: LPS treatment caused a moderate increase in c-Fos expression among the GLP-1 neurons within the DMd/IRt (* p < 0.05). The total number of GLP-1 neurons in the NTS and the DMd/IRt did not differ between groups.