Fig. 2.
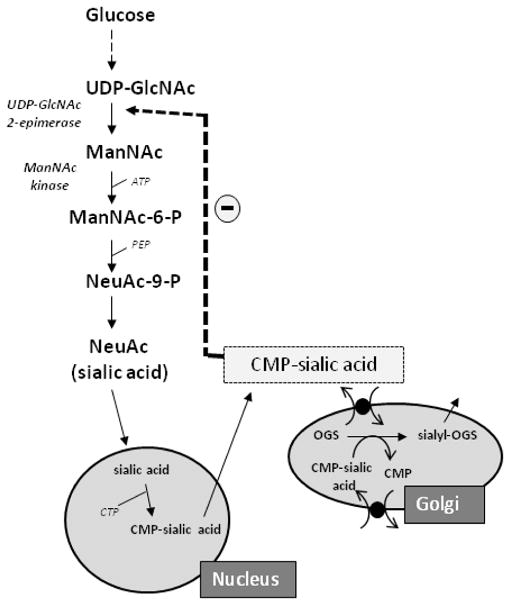
Sialic acid synthesis pathway. The biosynthesis of sialic acid (Neu5Ac) occurs in the cytosol, where glucose undergoes several modifications to become UDP-GlcNAc. The UDP-GlcNAC 2-epimerase activity of GNE/MNK then epimerises UDP-GlcNAc into ManNAc, after which its ManNAc kinase activity further converts this to ManNAc-6-P, which is then converted in several steps to the downstream product CMP-sialic acid. CMP-sialic acid is utilized by the Golgi complex to sialylate glycoconjugates. CMP-sialic acid can feedback-inhibit the UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase enzymatic activity in its allosteric site. For more details, see text.
