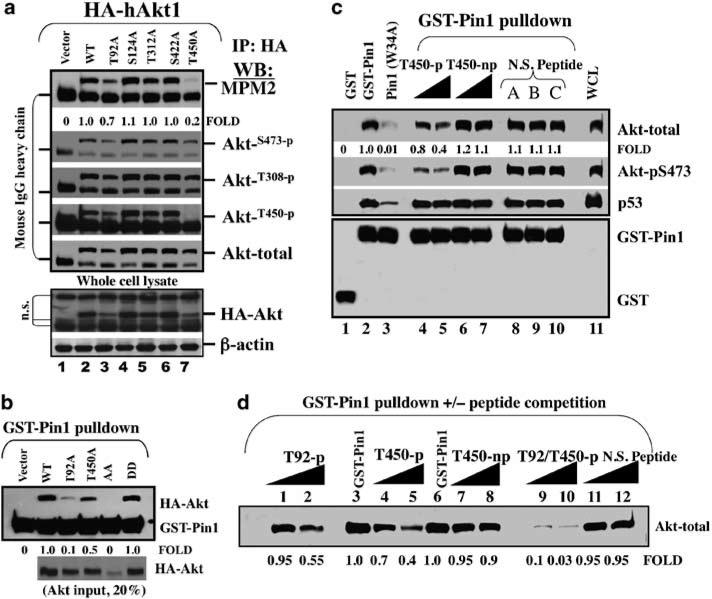
Figure 4.
Phosphorylation of Akt on the T92-Pro and T450-Pro sites is critical for the interaction between Pin1 and Akt. (a) Point mutation analysis of Akt Ser/Thr-Pro motifs identifies that mutation of T92 or T450 to T92A or T450A reduces Akt immunoreactivity toward anti-phosphorylated Ser/Thr-Pro motif antibody, MPM2, and anti-phospho-Akt antibodies (pS473 and pT308) in Akt1 (−/−) mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) cells. (b) A (glutathione-S-transferase) GST-Pin1 pull-down assay of HA-tagged wild-type human Akt1 or Akt1 with mutation of T92 or T450 or both. (c) GST-Pin1 pull-down assay of Akt in MDA-MB-468 cell lysate in the presence or absence of peptide competition with phosphorylated or non-phosphorylated T450 peptide as well as non-specific phosphopeptides (N.S. peptide A, B, and C). (d) GST-Pin1 pull-down and competition with a phosphorylated T92 peptide and/or T450 peptide.