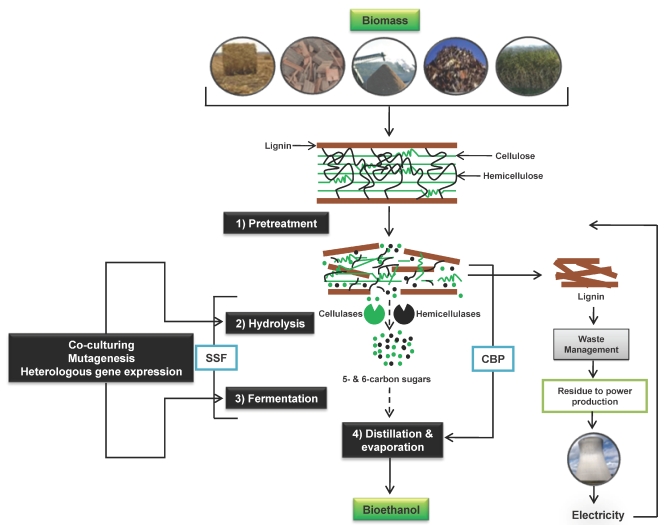
Figure 1.
Schematic picture for the conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to ethanol, including the major steps. Hydrolysis and fermentation can be performed separately (SHF, indicated by broken arrows) or as simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF). In consolidated bioprocessing (CBP) however, all bioconversion steps are minimized to one step in a single reactor using one or more microorganisms. Different techniques such as mutagenesis, co-culturing and heterologous gene expression have been used to improve sugars utilization of the microbial biocatalyst as well as activity and/or stability of hydrolytic fungal-derived enzymes in order to improve the overall yields. For reduction of production cost, ethanol production can be integrated with a combined heat and power plant using lignin.