Fig. (2).
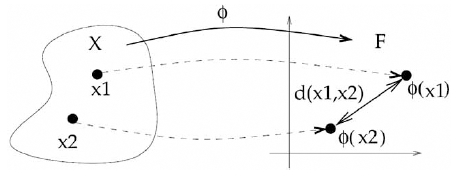
We can define the distance between two objects x1 and x2, such as two small molecules or proteins, as the Euclidean distance between their images Φ(x1) and Φ(x2). If the mapping Φ is defined by a valid kernel k, then this distance can be computed easily without computing Φ(x1) and Φ(x2), as shown in (2). This kernel trick can be extended to a variety of linear algorithms that only manipulate the data through inner products.
