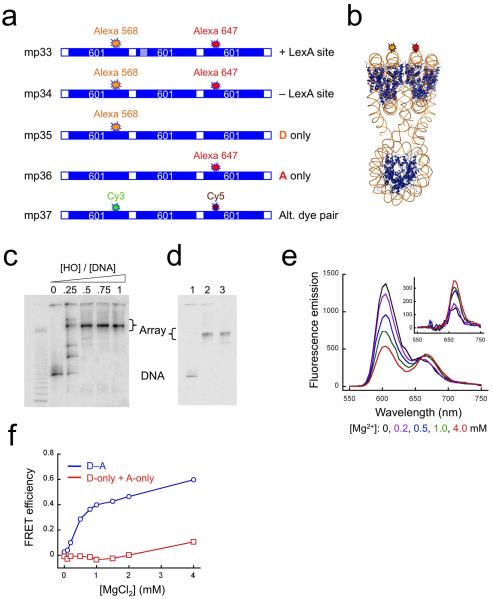
Figure 1. FRET analyses of nucleosome array compaction induced by Mg2+.
(a) Schematic illustrations of dye-labeled DNA constructs. “601” refers to the 147 bp-long nucleosome positioning sequence 60125,44; hatched boxes represent a specific target site for LexA protein; white boxes represent linker DNA; locations of the fluorescent donor dyes Alexa568 or Cy3, and of the acceptor dyes Alexa647 or Cy5 are indicated. (b) Expected 3-dimensional structure showing locations of the donor (orange) and acceptor (red) fluorophores. (c) Native gel analysis of the titration of 32P-labeled trinucleosome DNA with histone octamer, imaged by a Storm phosphorimager. The mass ratios of histone octamer (HO) to total DNA (including the competitor) are indicated. (d) Native gel analysis of a reconstitution reaction containing 5 μg of trinucleosome DNA, 15 μg of competitor DNA and 15 μg of HO, showing a fluorescence image of the Alexa647 dye. Lane 1, naked DNA; lane 2, after reconstitution; lane 3, after sucrose gradient purification. (e) Fluorescence spectra of the FRET labeled trinucleosomes assembled on DNA mp34 in 0.5x TE buffer plus 0-4.0 mM MgCl2. Inset: spectra after subtracting donor emission. (f) Absolute FRET efficiency from data of panel (e) (blue) and from a parallel titration of a mixture containing 50% donor-only and 50% acceptor-only labeled arrays (red), at the same total array concentration, as a control for aggregation.