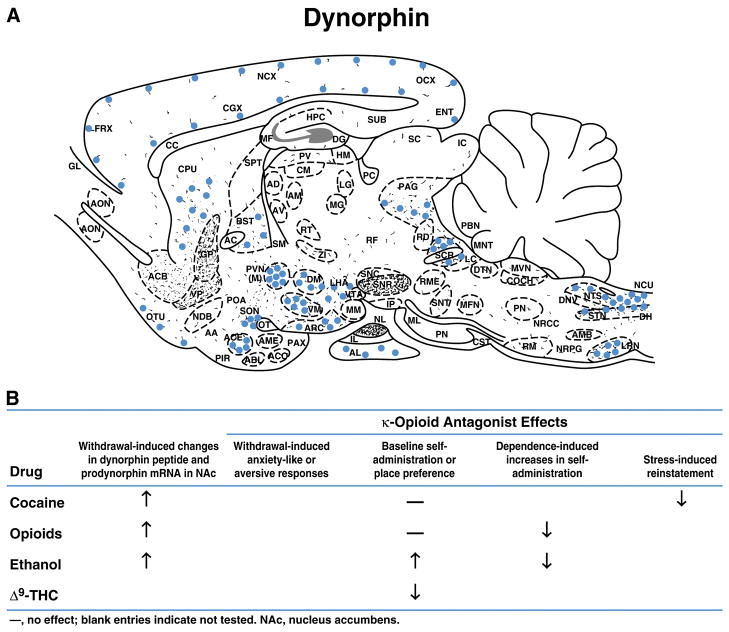
Figure 5. Localizations and Projections of Brain Stress Systems—Dynorphin.
(A) Schematic representation of the distribution of prodynorphin-derived peptides in the rat central nervous system determined by immunohistochemistry. Prodynorphin codes for several active opioid peptides containing the sequence of [Leu]enkephalin, including dynorphin A, dynorphin B, and α-neoendorphin. This precursor is distributed in neuronal systems found at all levels of the neuraxis. Like their proenkephalin counterparts, the prodynorphin neurons form both short-and long-tract projections often found in parallel with the proenkephalin systems. Neuronal perikarya are shown as solid circles, and fibers-terminals as short curved lines and dots. Modified with permission from Khachaturian et al. (1985). AA, anterior amygdala; ABL, basolateral nucleus of amygdala; AC, anterior commissure; ACB, nucleus accumbens; ACE, central nucleus of the amygdala; ACO, cortical nucleus of amygdala; AD, anterodorsal nucleus of thalamus; AL, anterior lobe of pituitary; AM, anteromedial nucleus of thalamus; AMB, nucleus ambiguus; AME, medial nucleus of the amygdala; AON, anterior olfactory nucleus; ARC, arcuate nucleus; AV, anteroventral nucleus of thalamus; BST, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; CC, corpus callosum; CGX, cingulate cortex; CM, central-medial nucleus of thalamus; COCH, cochlear nuclear complex; CPU, caudate-putamen; CST, corticospinal tract; DH, dorsal horn of spinal cord; DG, dentate gyrus; DM, dorsomedial nucleus of hypothalamus; DNV, dorsal motor nucleus of vagus; DTN, dorsal tegmental nucleus; ENT, entorhinal cortex; FN, fastigial nucleus of cerebellum; FRX, frontal cortex; GL, glomerular layer of olfactory bulb; GP, globus pallidus; HM, medial habenular nucleus; HPC, hippocampus; IC, inferior colliculus; IL, intermediate lobe of pituitary; IP, interpeduncular nuclear complex; LC, nucleus locus coeruleus; LG, lateral geniculate nucleus; LHA, lateral hypothalamic area; LRN, lateral reticular nucleus; MF, mossy fibers of hippocampus; MFN, motor facial nucleus; MG, medial geniculate nucleus; ML, medial lemniscus; MM, medial mammillary nucleus; MNT, mesencephalic nucleus of trigeminal; MVN, medial vestibular nucleus; NCU, nucleus cuneatus; NCX, neocortex; NDB, nucleus of diagonal band; NL, neural lobe of pituitary; NRGC, nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis; NRPG, nucleus reticularis paragigantocellularis; NTS, nucleus tractus solitarius; OCX, occipital cortex; OT, optic tract; OTU, olfactory tubercle; PAG, periaqueductal gray; PAX, periamygdaloid cortex; PBN, parabrachial nucleus; PC, posterior commissure; PIR, piriform cortex; PN, pons; POA, preoptic area; PP, perforant path; PV, periventricular nucleus of thalamus; PVN(M), paraventricular nucleus (pars magnocellularis); PVN(P), paraventricular nucleus (pars parvocellularis); RD, nucleus raphe dorsalis; RE, nucleus reuniens of thalamus; RF, reticular formation; RM, nucleus raphe magnus; RME, nucleus raphe medianus; SC, superior colliculus; SCP, superior cerebellar peduncle; SM, stria medullaris thalami; SNC, substantia nigra (pars compacta); SNR, substantia nigra (pars reticulata); SNT, sensory nucleus of trigeminal (main); SON, supraoptic nucleus; SPT, septal nuclei; STN, spinal nucleus of trigeminal; SUB, subiculum; VM, ventromedial nucleus of hypothalamus; VP, ventral pallidum; ZI, zona incerta.
(B) Role of dynorphin in dependence.