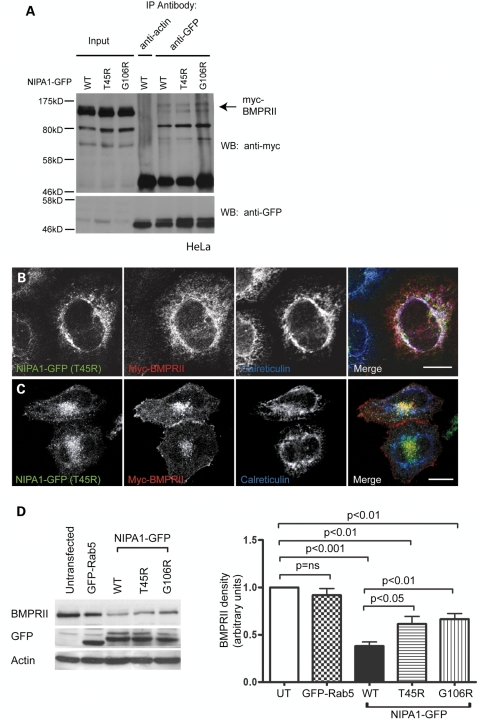
Figure 8.
Mutant NIPA1 interacts with BMPRII and alters its trafficking. (A) HeLa cells stably expressing wild-type or mutant forms of NIPA1-GFP and transiently transfected with myc-BMPRII were used in immunoprecipitation experiments with anti-GFP. Anti-actin was used as a control antibody in immunoprecipitation of the WT NIPA1-GFP sample. Total cell lysates (input lanes) and immunoprecipitated samples were then immunoblotted with anti-GFP or anti-myc. (B and C) HeLa cells stably expressing T45R NIPA1-GFP were transiently transfected with myc-BMPRII and labelled with the ER marker calreticulin. (B) A cell in which the mutant NIPA1, BMPRII and calreticulin show three-way co-localization. (C) A cell in which the BMPRII co-localizes with mutant NIPA1 in perinuclear puncta. (D) Representative experiment showing the effects of stable expression of WT or mutant forms of NIPA1-GFP on endogenous BMPRII concentration. A HeLa cell line stably expressing GFP-Rab5 was used as a control. GFP immunoblotting verified approximately equal expression levels of GFP-tagged proteins in respective cell lines, and actin immunoblotting verified equal loading. Quantitation of immunoblot band density in four such experiments is shown in the histogram. In the histograms, values were normalized to the value for the untransfected sample. Error bars: SEM. P-values were calculated using two-tailed paired t-tests.