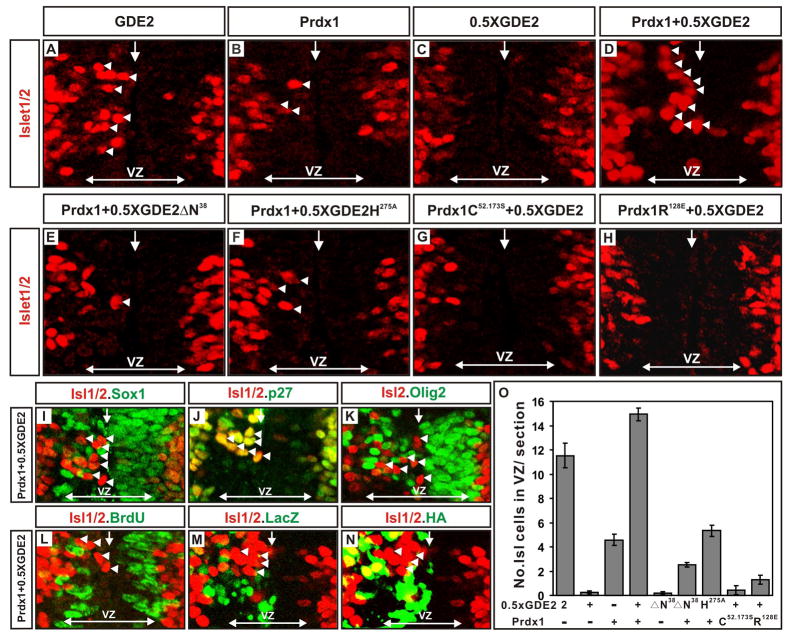
Figure 4. Prdx1/GDE2 complexes drive motor neuron differentiation in vivo.
(A–N) Immunohistochemical analyses of transverse sections of ventral St 19–20 chick spinal cords electroporated (left) with GDE2 and Prdx1. Arrowheads mark terminally differentiated neurons in the ventricular zone (VZ). The VZ was defined by BrdU pulse labeling to mark S-phase cells at lateral margins. Midline: vertical arrow, VZ: horizontal arrow. (M, N) Same section stained with HA and LacZ to detect Prdx1 and GDE2 respectively (O) Graph quantifying ectopic motor neurons in the VZ of electroporated embryos (mean ± s.e.m; n= 5–10). Prdx1 overexpression weakly induces ectopic motor neurons, presumably through interactions with GDE2 related proteins in VZ cells such as GDE6 (C.H. Lee and S. Sockanathan; unpublished observations).