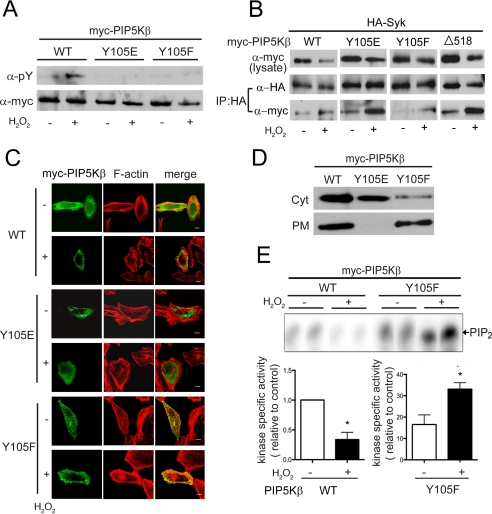
FIGURE 6.
Characterization of the PIP5KβY105 mutants. Cells transfected with WT or mutant PIP5Kβ were exposed to 1 mm H2O2 for 15 min. A, tyrosine phosphorylation. Myc-PIP5Kβs immunoprecipitated from COS cells were blotted with α-Tyr(P) and α-Myc. Data shown are representative of at least three experiments. B, association with Syk. COS cells were cotransfected with HA-Syk and Myc-PIP5Kβ. HA-Syk was immunoprecipitated and coimmunoprecipitated Myc-PIP5Kβ was detected by Western blotting. Data shown are representative of at least three experiments. C, subcellular distribution. HeLa cells overexpressing PIP5K WT or mutants were fixed and stained with α-Myc/FITC and TRITC-phalloidin (F-actin). Scale bars, 10 μm. D, membrane association. The PM-enriched and cytosolic (Cyt) fractions from COS cells were blotted with α-Myc. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments. E, in vitro lipid kinase activity. PIP5Kβ WT and Y105F were immunoprecipitated from control or H2O2-treated COS cells and assayed for lipid kinase activity in vitro. 32P-Labeled PIP2 were quantified after separation by TLC. Top, fluorogram from a representative experiment. Bottom, specific activity of the lipid kinases, calculated by normalizing the amount of [32P]PIP2 generated (in the linear range of the reaction) relative to the amount of Myc-PIP5Kβ used. The value for WT was defined as 1. Values shown are mean ± S.E. (n = 3).Asterisks denote statistically significant, with p < 0.05. Note the different scales used for the WT and Y105F samples. Error bars indicate S.E.M.